Safe procedure in endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors focused on preventing complications
- PMID: 20379999
- PMCID: PMC2852815
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i14.1688
Safe procedure in endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors focused on preventing complications
Abstract
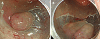
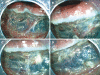
Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is efficient for en bloc resection of large colorectal tumors. However, it has several technical difficulties, because the wall of the colon is thin and due to the winding nature of the colon. The main complications of ESD comprise postoperative perforation and hemorrhage, similar to endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). In particular, the rate of perforation in ESD is higher than that in EMR. Perforation of the colon can cause fatal peritonitis. Endoscopic clipping is reported to be an efficient therapy for perforation. Most cases with perforation are treated conservatively without urgent surgical intervention. However, the rate of postoperative hemorrhage in ESD is similar to that in EMR. Endoscopic therapy including endoscopic clipping is performed and most of the cases are treated conservatively without blood transfusion. In blood examination, some degree of inflammation is detected after ESD. For the standardization of ESD, it is most important to decrease the rate of perforation. Adopting a safe strategy for ESD and a suitable choice of knife are both important ways of preventing perforation. Moreover, appropriate training and increasing experience can improve the endoscopic technique and can decrease the rate of perforation. In this review, we describe safe procedures in ESD to prevent complications, the complications of ESD and their management.
Figures


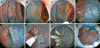
References
-
- Tanaka S, Haruma K, Oka S, Takahashi R, Kunihiro M, Kitadai Y, Yoshihara M, Shimamoto F, Chayama K. Clinicopathologic features and endoscopic treatment of superficially spreading colorectal neoplasms larger than 20 mm. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:62–66. - PubMed
-
- Saito Y, Fukuzawa M, Matsuda T, Fukunaga S, Sakamoto T, Uraoka T, Nakajima T, Ikehara H, Fu KI, Itoi T, et al. Clinical outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection of large colorectal tumors as determined by curative resection. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:343–352. - PubMed
-
- Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Iseki K, Narahara H, Uedo N, Sakai N, Ishikawa H, Otani T, Ishiguro S. Endoscopic piecemeal resection with submucosal saline injection of large sessile colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000;51:697–700. - PubMed
-
- Higaki S, Hashimoto S, Harada K, Nohara H, Saito Y, Gondo T, Okita K. Long-term follow-up of large flat colorectal tumors resected endoscopically. Endoscopy. 2003;35:845–849. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

