Suborganelle sensing of mitochondrial cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity
- PMID: 20380406
- PMCID: PMC2862470
- DOI: 10.1021/ja909652q
Suborganelle sensing of mitochondrial cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity
Abstract
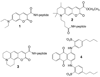
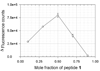
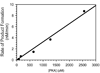
A fluorescent sensor of protein kinase activity has been developed and used to characterize the compartmentalized location of cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity in mitochondria. The sensor functions via a phosphorylation-induced release of a quencher from a peptide-based substrate, producing a 150-fold enhancement in fluorescence. The quenching phenomenon transpires via interaction of the quencher with Arg residues positioned on the peptide substrate. Although the cAMP-dependent protein kinase is known to be present in mitochondria, the relative amount of enzyme positioned in the major compartments (outer membrane, intermembrane space, and the matrix) of the organelle is unclear. The fluorescent sensor developed in this study was used to reveal the relative matrix/intermembrane space/outer membrane (85:6:9) distribution of PKA in bovine heart mitochondria.
Figures

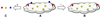


References
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Shabb JB. Chem Rev. 2001;101:2381–2411. - PubMed
-
- Smith FD, Langeberg LK, Scott JD. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:316–323. - PubMed
-
- Feliciello A, Gottesman ME, Avvedimento EV. Cell Signal. 2005;17:279–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

