The Selvester QRS Score is more accurate than Q waves and fragmented QRS complexes using the Mason-Likar configuration in estimating infarct volume in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 20381066
- PMCID: PMC2902677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2010.02.011
The Selvester QRS Score is more accurate than Q waves and fragmented QRS complexes using the Mason-Likar configuration in estimating infarct volume in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
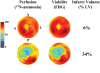
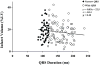
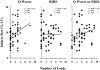
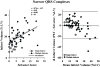
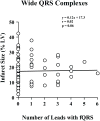
Infarct volume independently predicts cardiovascular events. Fragmented QRS complexes (fQRS) may complement Q waves for identifying infarction; however, their utility in advanced coronary disease is unknown. We tested whether fQRS could improve the electrocardiographic prediction of infarct volume by positron emission tomography in 138 patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ejection fraction, 0.27 +/- 0.09). Indices of infarction (pathologic Q waves, fQRS, and Selvester QRS Score) were analyzed by blinded observers. In patients with QRS duration less than 120 milliseconds, number of leads with pathologic Q waves (mean, 1.6 +/- 1.7) correlated weakly with infarct volume (r = 0.30, P < .05). Adding fQRS increased the number of affected leads (3.6 +/- 2.5), but the significant correlation with infarct volume was lost (r = 0.02, P = .10). Selvester Score was the most accurate (mean, 5.9 +/- 4.9 points; r = 0.49; P < .001). Fragmented QRS was not predictive of infarct size in patients with QRS duration of at least 120 milliseconds (r = 0.02, P = .19). Thus, in ischemic cardiomyopathy, consideration of fQRS complexes does not improve Q wave prediction of infarct volume; but Selvester Score was more accurate.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Feola M, Biggi A, Chauvie S, et al. Myocardial scar and insulin resistance predict cardiovascular events in severe ischaemic myocardial dysfunction: a perfusion-metabolism positron emission tomography study. Nucl Med Commun. 2008;29:448–54. - PubMed
-
- Beanlands RS, Ruddy TD, deKemp RA, et al. Positron emission tomography and recovery following revascularization (PARR-1): the importance of scar and the development of a prediction rule for the degree of recovery of left ventricular function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:1735–1743. - PubMed
-
- Allman KC, Shaw LJ, Hachamovitch R, Udelson JE. Myocardial viability testing and impact of revascularization on prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1151–1158. - PubMed
-
- Engblom H, Hedstrom E, Heiberg E, et al. Size and transmural extent of first-time reperfused myocardial infarction assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance can be estimated by 12-lead electrocardiogram. Am Heart J. 2005;150:920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

