Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids
- PMID: 20381137
- PMCID: PMC3024592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.024
Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids
Abstract
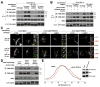
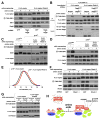
The mTORC1 kinase promotes growth in response to growth factors, energy levels, and amino acids, and its activity is often deregulated in disease. The Rag GTPases interact with mTORC1 and are proposed to activate it in response to amino acids by promoting mTORC1 translocation to a membrane-bound compartment that contains the mTORC1 activator, Rheb. We show that amino acids induce the movement of mTORC1 to lysosomal membranes, where the Rag proteins reside. A complex encoded by the MAPKSP1, ROBLD3, and c11orf59 genes, which we term Ragulator, interacts with the Rag GTPases, recruits them to lysosomes, and is essential for mTORC1 activation. Constitutive targeting of mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface is sufficient to render the mTORC1 pathway amino acid insensitive and independent of Rag and Ragulator, but not Rheb, function. Thus, Rag-Ragulator-mediated translocation of mTORC1 to lysosomal membranes is the key event in amino acid signaling to mTORC1.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Lysosomal Rag-ulation of mTOR complex 1 activity.Cell Metab. 2010 May 5;11(5):341-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.04.010. Cell Metab. 2010. PMID: 20444413
-
Cell signalling: Of Rags and Ragulator.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jun;11(6):388. doi: 10.1038/nrm2907. Epub 2010 May 6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20445544 No abstract available.
-
Signalling: Of Rags and Ragulator.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Jun;10(6):381. doi: 10.1038/nrc2863. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20506585 No abstract available.
References
-
- Binda M, Péli-Gulli M, Bonfils G, Panchaud N, Urban J, Sturgill T, Loewith R, De Virgilio C. The Vam6 GEF controls TORC1 by activating the EGO complex. Mol Cell. 2009;35:563–573. - PubMed
-
- Bohn G, Allroth A, Brandes G, Thiel J, Glocker E, Schäffer AA, Rathinam C, Taub N, Teis D, Zeidler C, et al. A novel human primary immunodeficiency syndrome caused by deficiency of the endosomal adaptor protein p14. Nat Med. 2006;13:38–45. - PubMed
-
- Buerger C, DeVries B, Stambolic V. Localization of Rheb to the endomembrane is critical for its signaling function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344:869–880. - PubMed
-
- Chavrier P, Parton RG, Hauri HP, Simons K, Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990;62:317–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

