E. coli NusG inhibits backtracking and accelerates pause-free transcription by promoting forward translocation of RNA polymerase
- PMID: 20381500
- PMCID: PMC2875378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.03.051
E. coli NusG inhibits backtracking and accelerates pause-free transcription by promoting forward translocation of RNA polymerase
Abstract
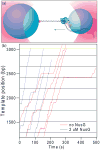
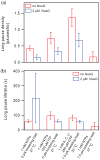
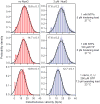
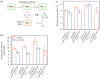
NusG is an essential transcription factor in Escherichia coli that is capable of increasing the overall rate of transcription. Transcript elongation by RNA polymerase (RNAP) is frequently interrupted by pauses of varying durations, and NusG is known to decrease the occupancy of at least some paused states. However, it has not been established whether NusG enhances transcription chiefly by (1) increasing the rate of elongation between pauses, (2) reducing the lifetimes of pauses, or (3) reducing the rate of entry into paused states. Here, we studied transcription by single molecules of RNAP under various conditions of ribonucleoside triphosphate concentration, applied load, and temperature, using an optical trapping assay capable of distinguishing pauses as brief as 1 s. We found that NusG increases the rate of elongation, that is, the pause-free velocity along the template. Because pauses are off-pathway states that compete with elongation, we observed a concomitant decrease in the rate of entry into short-lifetime, paused states. The effects on short pauses and elongation were comparatively modest, however. More dramatic was the effect of NusG on suppressing entry into long-lifetime ("stabilized") pauses. Because a significant fraction of the time required for the transcription of a typical gene may be occupied by long pauses, NusG is capable of exerting a significant modulatory effect on the rates of RNA synthesis. The observed properties of NusG were consistent with a unified model where the function of this accessory factor is to promote transcriptionally downstream motion of the enzyme along the DNA template, which has the effect of forward-biasing RNAP from the pre-translocated state toward the post-translocated state.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Robust regulation of transcription pausing in Escherichia coli by the ubiquitous elongation factor NusG.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 13;120(24):e2221114120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221114120. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37276387 Free PMC article.
-
NusG controls transcription pausing and RNA polymerase translocation throughout the Bacillus subtilis genome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 1;117(35):21628-21636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2006873117. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32817529 Free PMC article.
-
NusG-mediated Coupling of Transcription and Translation Enhances Gene Expression by Suppressing RNA Polymerase Backtracking.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 30;434(2):167330. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167330. Epub 2021 Oct 25. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34710399 Free PMC article.
-
The yin and yang of the universal transcription factor NusG.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2024 Oct;81:102540. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2024.102540. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39226817 Review.
-
Applying the brakes to transcription: regulation of gene expression by RNA polymerase pausing.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jul 24;207(7):e0008425. doi: 10.1128/jb.00084-25. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40476722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Factor-stimulated intrinsic termination: getting by with a little help from some friends.Transcription. 2022 Aug-Oct;13(4-5):96-108. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2127602. Epub 2022 Sep 25. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 36154805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NusG-dependent RNA polymerase pausing is a frequent function of this universally conserved transcription elongation factor.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Dec;55(6):716-728. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2020.1828261. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 33003953 Free PMC article.
-
NusG prevents transcriptional invasion of H-NS-silenced genes.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 7;15(10):e1008425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008425. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31589608 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanisms of Substrate Selection, Catalysis, and Translocation by the Elongating RNA Polymerase.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):3975-4006. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.05.042. Epub 2019 May 31. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31153902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase pausing and nascent-RNA structure formation are linked through clamp-domain movement.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;21(9):794-802. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2867. Epub 2014 Aug 10. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25108353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sullivan SL, Gottesman ME. Requirement for E. coli NusG protein in factor-dependent transcription termination. Cell. 1992;68:989–94. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Mason SW, Greenblatt J. Elongation factor NusG interacts with termination factor rho to regulate termination and antitermination of transcription. Genes Dev. 1993;7:161–72. - PubMed
-
- Nehrke KW, Platt T. A quaternary transcription termination complex. Reciprocal stabilization by Rho factor and NusG protein. J Mol Biol. 1994;243:830–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

