Targets and consequences of protein SUMOylation in neurons
- PMID: 20382182
- PMCID: PMC3310160
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.04.002
Targets and consequences of protein SUMOylation in neurons
Abstract
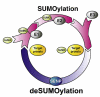
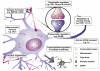
The post-translational modification of proteins is critical for the spatial and temporal regulation of signalling cascades. This is especially important in the CNS where the processes affecting differentiation, growth, targeting and communication between neurones are highly complex and very tightly regulated. In recent years it has emerged that modification of proteins by members of the SUMO (small ubiquitin-related modifier) family of proteins play key roles in neuronal function. SUMOylation involves the covalent conjugation of a member of the SUMO family to lysine residues in target proteins. Multiple nuclear and perinuclear SUMOylation targets have been reported to be involved in nuclear organisation and transcriptional regulation. In addition, a growing number of extranuclear SUMO substrates have been identified that can have important acute effects on neuronal function. The SUMOylation of both intra- and extranuclear proteins have been implicated in a diverse array of processes that have far-reaching implications for neuronal function and pathophysiology. Here we review the current understanding of the targets and consequences of protein SUMOylation in the brain and examine its established and potential involvement in a wide range of neurological and neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging extranuclear roles of protein SUMOylation in neuronal function and dysfunction.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007 Dec;8(12):948-59. doi: 10.1038/nrn2276. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17987030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumoylation: Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:261-281. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197918 Review.
-
Mechanisms, regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation.Biochem J. 2010 May 13;428(2):133-45. doi: 10.1042/BJ20100158. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20462400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhes, a striatal enriched protein, regulates post-translational small-ubiquitin-like-modifier (SUMO) modification of nuclear proteins and alters gene expression.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Apr 8;81(1):169. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05181-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38589732 Free PMC article.
-
Protein SUMOylation in neuropathological conditions.Drug News Perspect. 2009 Jun;22(5):255-65. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2009.22.5.1378636. Drug News Perspect. 2009. PMID: 19609463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PIAS1 Regulates Mutant Huntingtin Accumulation and Huntington's Disease-Associated Phenotypes In Vivo.Neuron. 2016 May 4;90(3):507-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.016. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27146268 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of metabotropic glutamate receptor C-terminal domains in contact with interacting proteins.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Apr 23;5:52. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00052. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22536173 Free PMC article.
-
A discovery resource of rare copy number variations in individuals with autism spectrum disorder.G3 (Bethesda). 2012 Dec;2(12):1665-85. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004689. Epub 2012 Dec 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2012. PMID: 23275889 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Post-Translational Modifications in Regulating the Development and Progression of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jul;60(7):3617-3632. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03277-z. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36877359 Review.
-
Agonist-induced PKC phosphorylation regulates GluK2 SUMOylation and kainate receptor endocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 6;108(49):19772-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111575108. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22089239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agbor TA, Taylor CT. SUMO, hypoxia and the regulation of metabolism. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008;36:445–448. - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Flier JS. Leptin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2000;62:413–437. - PubMed
-
- Ahn K, Song JH, Kim DK, Park MH, Jo SA, Koh YH. Ubc9 gene polymorphisms and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the Korean population: a genetic association study. Neurosci. Lett. 2009;465:272–275. - PubMed
-
- Appella E, Anderson CW. Post-translational modifications and activation of p53 by genotoxic stresses. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001;268:2764–2772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

