Constructs of human neuropathy target esterase catalytic domain containing mutations related to motor neuron disease have altered enzymatic properties
- PMID: 20382209
- PMCID: PMC4310459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.03.1120
Constructs of human neuropathy target esterase catalytic domain containing mutations related to motor neuron disease have altered enzymatic properties
Abstract
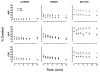
Neuropathy target esterase (NTE) is a phospholipase/lysophospholipase associated with organophosphorus (OP) compound-induced delayed neurotoxicity (OPIDN). Distal degeneration of motor axons occurs in both OPIDN and the hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSPs). Recently, mutations within the esterase domain of NTE were identified in patients with a novel type of HSP (SPG39) designated NTE-related motor neuron disease (NTE-MND). Two of these mutations, arginine 890 to histidine (R890H) and methionine 1012 to valine (M1012V), were created in human recombinant NTE catalytic domain (NEST) to measure possible changes in catalytic properties. These mutated enzymes had decreased specific activities for hydrolysis of the artificial substrate, phenyl valerate. In addition, the M1012V mutant exhibited a reduced bimolecular rate constant of inhibition (k(i)) for all three inhibitors tested: mipafox, diisopropylphosphorofluoridate, and chlorpyrifos oxon. Finally, while both mutated enzymes inhibited by OP compounds exhibited altered time-dependent loss of their ability to be reactivated by nucleophiles (aging), more pronounced effects were seen with the M1012V mutant. Taken together, the results from specific activity, inhibition, and aging experiments suggest that the mutations found in association with NTE-MND have functional correlates in altered enzymological properties of NTE.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Aldridge WN, Reiner E. Enzyme Inhibitors as Substrates: Interactions of Esterases with Esters of Organophosphorus and Carbamic Acids. North-Holland Publishing; Amsterdam: 1972.
-
- Atkins J, Glynn P. Membrane association of and critical residues in the catalytic domain of human neuropathy target esterase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:24477–24483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

