Prostaglandin E2 potentiates heat shock-induced heat shock protein 72 expression in A549 cells
- PMID: 20382255
- PMCID: PMC2919605
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2010.03.006
Prostaglandin E2 potentiates heat shock-induced heat shock protein 72 expression in A549 cells
Abstract
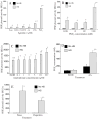
The heat shock (HS) response is an important cytoprotective response comprising the expression of heat shock proteins (HSPs) and orchestrated by the heat/stress-induced transcription factor, heat shock factor-1 (HSF-1). Previous studies suggest that the activation threshold and magnitude of the HS response may be modified by treatment with arachidonic acid (AA). We analyzed the effect of exogenous AA and its metabolites, PGE(2), LTD(4), and 15-HETE on HSF-1-dependent gene expression in A549 human respiratory epithelial-like cells. When added at 1microM, PGE(2) much more than LTD(4), but not 15-HETE increased activity of a synthetic HSF-1-dependent reporter after HS exposure (42 degrees C for 2h), but had no effect in the absence of HS. Exposing A549 cells to HS stimulated the release of PGE(2) and treatment with the cyclooxygenase inhibitor, ibuprofen, reduced HS-induced HSF-1-dependent transcription. PGE(2) increased HS-induced HSP72 mRNA and protein expression but EMSA and Western blot analysis failed to show an effect on HSF-1 DNA binding activity or post-translational modification. In summary, we showed that HS stimulates the generation of PGE(2), which augments the generation of HSPs. The clinical consequences of this pathway have yet to be determined.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Feder ME, Hofmann GE. Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:243–82. - PubMed
-
- Sarge KD, Murphy SP, Morimoto RI. Activation of heat shock gene transcription by heat shock factor 1 involves oligomerization, acquisition of DNA-binding activity, and nuclear localization and can occur in the absence of stress [published errata appear in Mol Cell Biol 1993 May;13(5):3122–3 and 1993 Jun;13(6):3838–9] Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13(3):1392–407. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McMillan DR, Xiao X, Shao L, Graves K, Benjamin IJ. Targeted disruption of heat shock transcription factor 1 abolishes thermotolerance and protection against heat-inducible apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(13):7523–8. - PubMed
-
- Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin ASJscx, et al. TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Science. 1996;274:784–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

