Circulating endothelial progenitor cells are not affected by acute systemic inflammation
- PMID: 20382859
- PMCID: PMC2886634
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00921.2009
Circulating endothelial progenitor cells are not affected by acute systemic inflammation
Abstract
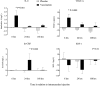
Vascular injury causes acute systemic inflammation and mobilizes endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and endothelial cell (EC) colony-forming units (EC-CFUs). Whether such mobilization occurs as part of a nonspecific acute phase response or is a phenomenon specific to vascular injury remains unclear. We aimed to determine the effect of acute systemic inflammation on EPCs and EC-CFU mobilization in the absence of vascular injury. Salmonella typhus vaccination was used as a model of acute systemic inflammation. In a double-blind randomized crossover study, 12 healthy volunteers received S. typhus vaccination or placebo. Phenotypic EPC populations enumerated by flow cytometry [CD34(+)VEGF receptor (VEGF)R-2(+)CD133(+), CD14(+)VEGFR-2(+)Tie2(+), CD45(-)CD34(+), as a surrogate for late outgrowth EPCs, and CD34(+)CXCR-4(+)], EC-CFUs, and serum cytokine concentrations (high sensitivity C-reactive protein, IL-6, and stromal-derived factor-1) were quantified during the first 7 days. Vaccination increased circulating leukocyte (9.8 + or - 0.6 vs. 5.1 + or - 0.2 x 10(9) cells/l, P < 0.0001), serum IL-6 [0.95 (0-1.7) vs. 0 (0-0) ng/l, P = 0.016], and VEGF-A [60 (45-94) vs. 43 (21-64) pg/l, P = 0.006] concentrations at 6 h and serum high sensitivity C-reactive protein at 24 h [2.7 (1.4-3.6) vs. 0.4 (0.2-0.8) mg/l, P = 0.037]. Vaccination caused a 56.7 + or - 7.6% increase in CD14(+) cells at 6 h (P < 0.001) and a 22.4 + or - 6.9% increase in CD34(+) cells at 7 days (P = 0.04). EC-CFUs, putative vascular progenitors, and the serum stromal-derived factor-1 concentration were unaffected throughout the study period (P > 0.05 for all). In conclusion, acute systemic inflammation causes nonspecific mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells, although it does not selectively mobilize putative vascular progenitors. We suggest that systemic inflammation is not the primary stimulus for EPC mobilization after acute vascular injury.
Figures


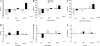


Similar articles
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilizes functional endothelial progenitor cells in patients with coronary artery disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Feb;25(2):296-301. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000151690.43777.e4. Epub 2004 Nov 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15569821 Clinical Trial.
-
Differentiation and expansion of endothelial cells from human bone marrow CD133(+) cells.Br J Haematol. 2001 Oct;115(1):186-94. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.03077.x. Br J Haematol. 2001. PMID: 11722432
-
Inhaled NO contributes to lung repair in piglets with acute respiratory distress syndrome via increasing circulating endothelial progenitor cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033859. Epub 2012 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22448277 Free PMC article.
-
Human CD34+AC133+VEGFR-2+ cells are not endothelial progenitor cells but distinct, primitive hematopoietic progenitors.Exp Hematol. 2007 Jul;35(7):1109-18. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.04.002. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17588480
-
Increased circulating hematopoietic and endothelial progenitor cells in the early phase of acute myocardial infarction.Blood. 2005 Jan 1;105(1):199-206. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-05-1831. Epub 2004 Sep 2. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15345590
Cited by
-
Extrarenal Progenitor Cells Do Not Contribute to Renal Endothelial Repair.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jun;27(6):1714-26. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015030321. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26453608 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum levels of fractalkine and mobilisation of CD34+CD45- endothelial progenitor cells in systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Mar 20;19(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1271-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28320472 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous coronary intervention causes a rapid but transient mobilisation of CD34(+)CD45(-) cells.Open Heart. 2014 Aug 20;1(1):e000047. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2014-000047. eCollection 2014. Open Heart. 2014. PMID: 25332796 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing effects of monomeric and pentameric C-reactive protein on endothelial progenitor cells.Basic Res Cardiol. 2011 Sep;106(5):879-95. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0191-y. Epub 2011 May 12. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21562922 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistological localization of endogenous unlabeled stem cells in wounded skin.J Histochem Cytochem. 2014 Apr;62(4):276-85. doi: 10.1369/0022155414520710. Epub 2014 Jan 7. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014. PMID: 24399040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ablin JN, Boguslavski V, Aloush V, Elkayam O, Paran D, Caspi D, George J. Effect of anti-TNFα treatment on circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci 79: 2364–2369, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Adams V, Lenk K, Linke A, Lenz D, Erbs S, Sandri M, Tarnok A, Gielen S, Emmrich F, Schuler G, Hambrecht R. Increase of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with coronary artery disease after exercise-induced ischemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24: 684–690, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der Zee R, Li T, Witzenbichler B, Schatteman G, Isner JM. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 275: 964–966, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Banerjee S, Brilakis E, Zhang S, Roesle M, Lindsey J, Philips B, Blewett CG, Terada LS. Endothelial progenitor cell mobilization after percutaneous coronary intervention. Atherosclerosis 189: 70–75, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

