X-ray structure and characterization of carbamate kinase from the human parasite Giardia lamblia
- PMID: 20383005
- PMCID: PMC2852327
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309110004665
X-ray structure and characterization of carbamate kinase from the human parasite Giardia lamblia
Abstract
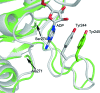
Carbamate kinase catalyzes the reversible conversion of carbamoyl phosphate and ADP to ATP and ammonium carbamate, which is hydrolyzed to ammonia and carbonate. The three-dimensional structure of carbamate kinase from the human parasite Giardia lamblia (glCK) has been determined at 3 A resolution. The crystals belonged to the monoclinic space group P2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 69.77, b = 85.41, c = 102.1 A, beta = 106.8 degrees . The structure was refined to a final R factor of 0.227. The essentiality of glCK together with its absence in humans makes the enzyme an attractive candidate for anti-Giardia drug development. Steady-state kinetic rate constants have been determined. The k(cat) for ATP formation is 319 +/- 9 s(-1). The K(m) values for carbamoyl phosphate and ADP are 85 +/- 6 and 70 +/- 5 microM, respectively. The structure suggests that three invariant lysine residues (Lys131, Lys216 and Lys278) may be involved in the binding of substrates and phosphoryl transfer. The structure of glCK reveals that a glycerol molecule binds in the likely carbamoyl phosphate-binding site.
Figures
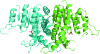

Similar articles
-
Structural basis for inactivation of Giardia lamblia carbamate kinase by disulfiram.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10502-10509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553123. Epub 2014 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24558036 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of carbamate kinase from Giardia lamblia bound with citric acid and AMP-PNP.PLoS One. 2013 May 20;8(5):e64004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064004. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23700444 Free PMC article.
-
The 1.5 A resolution crystal structure of the carbamate kinase-like carbamoyl phosphate synthetase from the hyperthermophilic Archaeon pyrococcus furiosus, bound to ADP, confirms that this thermostable enzyme is a carbamate kinase, and provides insight into substrate binding and stability in carbamate kinases.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jun 2;299(2):463-76. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3779. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10860751
-
The carbamoyl-phosphate synthase family and carbamate kinase: structure-function studies.Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Nov;23(4):879-83. doi: 10.1042/bst0230879. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995. PMID: 8654858 Review. No abstract available.
-
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: a crooked path from substrates to products.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998 Oct;2(5):624-32. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(98)80094-x. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1998. PMID: 9818189 Review.
Cited by
-
A homogenous luminescence assay reveals novel inhibitors for giardia lamblia carbamate kinase.Curr Chem Genomics. 2012;6:93-102. doi: 10.2174/1875397301206010093. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Curr Chem Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23400734 Free PMC article.
-
The ybcF Gene of Escherichia coli Encodes a Local Orphan Enzyme, Catabolic Carbamate Kinase.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 28;32(12):1527-1536. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2210.10037. Epub 2022 Nov 7. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36384810 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characterization of the enzymes composing the arginine deiminase pathway in Mycoplasma penetrans.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047886. Epub 2012 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23082227 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for inactivation of Giardia lamblia carbamate kinase by disulfiram.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10502-10509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553123. Epub 2014 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24558036 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of carbamate kinase from Giardia lamblia bound with citric acid and AMP-PNP.PLoS One. 2013 May 20;8(5):e64004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064004. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23700444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biagini, G. A., Yarlett, N., Ball, G. E., Billetz, A. C., Lindmark, D. G., Martinez, M. P., Lloyd, D. & Edwards, M. R. (2003). Mol. Biochem. Parasitol.128, 11–19. - PubMed
-
- Brünger, A. T., Adams, P. D., Clore, G. M., DeLano, W. L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Jiang, J.-S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N. S., Read, R. J., Rice, L. M., Simonson, T. & Warren, G. L. (1998). Acta Cryst. D54, 905–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

