Dissection of host cell signal transduction during Acinetobacter baumannii-triggered inflammatory response
- PMID: 20383325
- PMCID: PMC2850920
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010033
Dissection of host cell signal transduction during Acinetobacter baumannii-triggered inflammatory response
Abstract
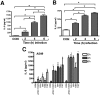
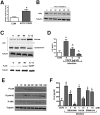
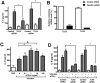
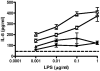
Infected airway epithelial cells up-regulate the expression of chemokines, chiefly IL-8, and antimicrobial molecules including beta-defensins (BD). Acinetobacter baumannii is a cause of hospital-acquired pneumonia. We examined whether A. baumannii induced the expressions of IL-8 and BD2 by airway epithelial cells and the receptors implicated in bacterial detection. A549 and human primary airway cells released IL-8 upon infection. A. baumannii-infected cells also increased the expression of BD2 which killed A. baummannii strains. IL-8 induction was via NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated kinases p38 and p44/42-dependent pathways. A. baumannii engaged Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 pathways and A549 cells could use soluble CD14 as TLRs co-receptor. A. baumannii lipopolysaccharide stimulated IL-8 release by A549 cells and sCD14 facilitated the recognition of the lipopolysaccharide. Mass spectrometry analysis revealed that A. baumannii lipid A structure matches those with endotoxic potential. These results demonstrate that airway epithelial cells produce mediators important for A. baumannii clearance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
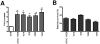
Similar articles
-
The Nod1, Nod2, and Rip2 axis contributes to host immune defense against intracellular Acinetobacter baumannii infection.Infect Immun. 2014 Mar;82(3):1112-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01459-13. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24366254 Free PMC article.
-
Acinetobacter baumannii lipopolysaccharides are potent stimulators of human monocyte activation via Toll-like receptor 4 signalling.J Med Microbiol. 2007 Feb;56(Pt 2):165-171. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46823-0. J Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17244795
-
IL-33 Treatment Attenuates the Systemic Inflammation Reaction in Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia by Suppressing TLR4/NF-κB Signaling.Inflammation. 2018 Jun;41(3):870-877. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0741-7. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29508184
-
Tug of war between Acinetobacter baumannii and host immune responses.Pathog Dis. 2018 Dec 1;76(9):ftz004. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftz004. Pathog Dis. 2018. PMID: 30657912 Review.
-
Innate Immune Responses to Acinetobacter baumannii in the Airway.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019 Aug;39(8):441-449. doi: 10.1089/jir.2019.0008. Epub 2019 Apr 23. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019. PMID: 31013462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of macrophages in early host resistance to respiratory Acinetobacter baumannii infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40019. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040019. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768201 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-associated changes in the enteric microbial community: potential role in loss of homeostasis and development of systemic inflammation.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017 Feb;30(1):31-43. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000341. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27922852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCL20 and Beta-Defensin 2 Production by Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Macrophages in Response to Brucella abortus Infection.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 8;10(10):e0140408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140408. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26448160 Free PMC article.
-
Host Innate Immune Responses to Acinetobacter baumannii Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 14;10:486. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00486. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33042864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoethanolamine modification of lipid A in colistin-resistant variants of Acinetobacter baumannii mediated by the pmrAB two-component regulatory system.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Jul;55(7):3370-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00079-11. Epub 2011 May 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21576434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fagon JY, Chastre J, Domart Y, Trouillet JL, Gibert C. Mortality due to ventilator-associated pneumonia or colonization with Pseudomonas or Acinetobacter species: assessment by quantitative culture of samples obtained by a protected specimen brush. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;23:538–542. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino Y, Mio T, Nagai S, Miki H, Ito I, Izumi T. Cytotoxic effects of cigarette smoke extract on an alveolar type II cell-derived cell line. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001;281:L509–L516. - PubMed
-
- Mio T, Romberger DJ, Thompson AB, Robbins RA, Heires A, et al. Cigarette smoke induces interleukin-8 release from human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;155:1770–1776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

