Aquaporin expression in blood-retinal barrier cells during experimental autoimmune uveitis
- PMID: 20383338
- PMCID: PMC2850934
Aquaporin expression in blood-retinal barrier cells during experimental autoimmune uveitis
Abstract
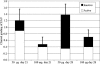
Purpose: Blood-retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown and retinal edema are major complications of autoimmune uveitis and could be related to deregulation of aquaporin (AQP) expression. We have therefore evaluated the expression of AQP1 and AQP4 on BRB cells during experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) in mice.
Methods: C57Bl6 mice were immunized with interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) peptide 1-16. The disease was graded clinically, and double immunolabeling using glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP; a marker of disease activity) and AQP1 or AQP4 antibodies was performed at day 28. AQP1 expression was also investigated in mouse retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells (B6-RPE07 cell line) by reverse transcriptase PCR and western blot under basal and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-stimulated conditions.
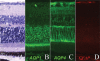
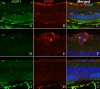
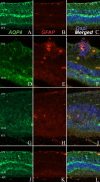
Results: In both normal and EAU retina, AQP1 and AQP4 expression were restricted to the photoreceptor layer and to the Müller cells, respectively. Retinal endothelial cells never expressed AQP1. In vasculitis and intraretinal inflammatory infiltrates, decreased AQP1 expression was observed due to the loss of photoreceptors and the characteristic radial labeling of AQP4 was lost. On the other hand, no AQP4 expression was detected in RPE cells. AQP1 was strongly expressed by choroidal endothelial cells, rendering difficult the evaluation of AQP1 expression by RPE cells in vivo. No major differences were found between EAU and controls at this level. Interestingly, B6-RPE07 cells expressed AQP1 in vitro, and TNF-alpha downregulated AQP1 protein expression in those cells.
Conclusions: Changes in retinal expression of AQP1 and AQP4 during EAU were primarily due to inflammatory lesions, contrasting with major modulation of AQP expression in BRB detected in other models of BRB breakdown. However, our data showed that TNF-alpha treatment strongly modulates AQP1 expression in B6-RPE07 cells in vitro.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High salt loading alters the expression and localization of glial aquaporins in rat retina.Exp Eye Res. 2009 Jun 15;89(1):88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.02.017. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Exp Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19268466
-
Glio-vascular modifications caused by Aquaporin-4 deletion in the mouse retina.Exp Eye Res. 2016 May;146:259-268. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 27018215
-
High-salt loading exacerbates increased retinal content of aquaporins AQP1 and AQP4 in rats with diabetic retinopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2009 Nov;89(5):741-7. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.06.020. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Exp Eye Res. 2009. PMID: 19596320
-
Shifting from ependyma to choroid plexus epithelium and the changing expressions of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4.J Physiol. 2024 Jul;602(13):3097-3110. doi: 10.1113/JP284196. Epub 2023 Nov 17. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37975746 Review.
-
Blood-retina barrier dysfunction in experimental autoimmune uveitis: the pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.Anat Cell Biol. 2022 Mar 31;55(1):20-27. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.227. Anat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35354673 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aquaporin-4 triggers inflammation in a murine endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) model.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04192-8. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40597858 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α in Uveitis: From Bench to Clinic.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 2;12:740057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.740057. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34795583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High glucose promotes the migration of retinal pigment epithelial cells through increased oxidative stress and PEDF expression.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;311(3):C418-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2016. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27440660 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin-1 attenuates macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses by inhibiting p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury.Inflamm Res. 2019 Dec;68(12):1035-1047. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01285-1. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31529146 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in the eye: expression, function, and roles in ocular disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1840(5):1513-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.10.037. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24184915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wakefield D, Chang JH.Epidemiology of uveitisInt Ophthalmol Clin 2005451–13. - PubMed
-
- de Smet MD, Chan CC. Regulation of ocular inflammation - what experimental and human studies have taught us. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001;20:761–97. - PubMed
-
- Lardenoye CWTA, van Kooij B, Rothova A. Impact of macular edema on visual acuity in uveitis. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:1446–9. - PubMed
-
- Bringmann A, Reichenbach A, Wiedemann P. Pathomechanisms of cystoid macular edema. Ophthalmic Res. 2004;36:241–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
