Caffeine enhances radiosensitization to orthotopic transplant LM3 hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo
- PMID: 20384627
- PMCID: PMC11158075
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01564.x
Caffeine enhances radiosensitization to orthotopic transplant LM3 hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo
Abstract
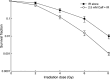
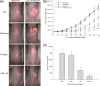
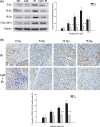
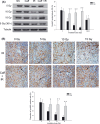
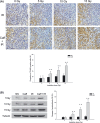
The aim of this study was to determine whether caffeine enhanced radiosensitization in an orthotopic transplant of LM3 human hepatocellular cancer in nude mice. LM3 hepatocellular carcinoma cells were infected with red fluorescent protein and irradiated, and cell cycle distribution and survival fraction were detected. A nude mouse model of orthotopic transplant of red fluorescent protein-expressing LM3 hepatocellular cancer was established. Nude mice were divided into four groups: control (NS); caffeine (Caff) alone; irradiation (IR) alone; and caffeine + IR (Caff + IR). Tumor growth curves were described. Expression of cyclin and apoptosis were evaluated by analysis of phosphorylated cyclin dependent kinase 1 (CDC2) Tyr15 (CDC2-Tyr15-P), cyclinB1, TUNEL staining, and caspase-3. Caffeine abrogated IR-induced G(2) phase arrest and decreased survival of irradiated LM3 cells. Caffeine enhanced radiosensitivity of LM3 hepatocellular cancer in vivo. Tumor growth delay time in the Caff + IR group was 14.3 days compared with the NS group, 14.1 days compared with the Caff alone group, and 7.2 days compared with the IR alone group. At 15 Gy, expression of CDC2-Tyr15-P in the Caff + IR group (26.0 +/- 8.9%) was significantly lower than in the IR alone group (68.4 +/- 10.6%), expression of cyclinB1 and proportion of TUNEL-positive cells in the Caff + IR group (30.4 +/- 8.7% and 59.2 +/- 9.5%, respectively) was significantly higher than in the IR alone group (7.0 +/- 3.7% and 24.2 +/- 7.2%, respectively), expression of caspase-3 was consistent with the TUNEL staining results. This study suggested that caffeine might enhance the radiosensitivity of LM3 hepatocellular cancer in vivo, and may be feasible for further clinical applications.
Figures

References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2005; 55: 74–108. - PubMed
-
- Mornex F, Girard N, Beziat C et al. Feasibility and efficacy of high‐dose three‐dimensional‐conformal radiotherapy in cirrhotic patients with small‐size hepatocellular carcinoma non‐eligible for curative therapies – mature results of the French Phase II RTF‐1 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006; 66: 1152–8. - PubMed
-
- Zeng ZC, Tang ZY, Fan J et al. A comparison of chemoembolization combination with and without radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer J (Sudbury, Mass.) 2004; 10: 307–16. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi K, Mitsuhashi N, Saitoh J et al. Caffeine enhanced radiosensitivity of rat tumor cells with a mutant‐type p53 by inducing apoptosis in a p53‐independent manner. Cancer Lett 2000; 152: 157–62. - PubMed
-
- Yao SL, Akhtar AJ, McKenna KA et al. Selective radiosensitization of p53‐deficient cells by caffeine‐mediated activation of p34cdc2 kinase. Nat Med 1996; 2: 1140–3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

