Histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells to 5-FU/S-1 via down-regulation of thymidylate synthase expression and up-regulation of p21(waf1/cip1) expression
- PMID: 20384633
- PMCID: PMC11159244
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01559.x
Histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells to 5-FU/S-1 via down-regulation of thymidylate synthase expression and up-regulation of p21(waf1/cip1) expression
Abstract
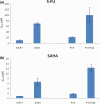
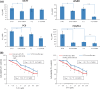
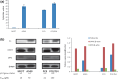
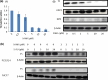
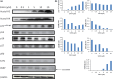
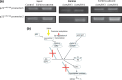
It is desirable to find more appropriate therapeutic opportunities in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) due to the current poor prognosis of affected patients. Recently, several histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, including suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), have been reported to exhibit antitumor activities against NSCLC. S-1, a novel oral fluorouracil anticancer drug, has been developed for clinical use in the treatment of NSCLC in Japan. Using an MTT assay, we analyzed the growth-inhibitory effect of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), S-1, and SAHA against three NSCLC cell lines, as well as the breast cancer cell line MCF7 which is known to be highly sensitive to 5-FU. Combined treatment with low-dose SAHA enhanced 5-FU- and S-1-mediated cytotoxicity and resulted in synergistic effects, especially in 5-FU-resistant cells. Both the mRNA and protein expression levels of thymidylate synthase (TS), dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), and orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRT), which are associated with 5-FU sensitivity/response, were analyzed in the cells undergoing treatment. 5-Fluorouracil-resistant lung cancer cells displayed high expression of TS mRNA and protein. Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid down-regulated TS mRNA and protein expression, as well as repressed the rapid induction of this factor during 5-FU treatment, in all examined cell types. We also examined the status of the Rb-E2F1 pathway, with SAHA up-regulating p21(waf1/cip1) expression via promoter histone acetylation; this, in turn, blocked the Rb-E2F1 pathway. We conclude that combination therapy with SAHA and S-1 in lung cancer may be promising due to its potential to overcome S-1 resistance via modulation of 5-FU/S-1 sensitivity-associated biomarker (TS) by HDAC inhibitor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances 5-fluorouracil cytotoxicity by down-regulating thymidylate synthase in human cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Dec;5(12):3085-95. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0419. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 17172411
-
The role of thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in resistance to 5-fluorouracil in human lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2005 Sep;49(3):345-51. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.05.003. Lung Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15993511
-
Synergistic antitumor effect of combined 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) with 5-chloro-2,4-dihydroxypyridine on 5-FU-resistant gastric cancer cells: possible role of a dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase-independent mechanism.J Gastroenterol. 2007 Oct;42(10):816-22. doi: 10.1007/s00535-007-2101-5. Epub 2007 Oct 15. J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17940834
-
UFT and S-1 for treatment of primary lung cancer.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010 Jan;58(1):3-13. doi: 10.1007/s11748-009-0498-x. Epub 2010 Jan 9. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20058135 Review.
-
The natural tumor suppressor protein maspin and potential application in non small cell lung cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2010 Jun;16(16):1877-81. doi: 10.2174/138161210791208974. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20337574 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A randomized, double-blind, phase II study of oral histone deacetylase inhibitor resminostat plus S-1 versus placebo plus S-1 in biliary tract cancers previously treated with gemcitabine plus platinum-based chemotherapy.Cancer Med. 2021 Mar;10(6):2088-2099. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3813. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33635605 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Histone deacetylases as targets for treatment of multiple diseases.Clin Sci (Lond). 2013 Jun;124(11):651-62. doi: 10.1042/CS20120504. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23414309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of P21 in Resistance of Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 20;23(7):597-602. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.16. Epub 2020 May 21. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32434295 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Enhancement of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by 5-fluorouracil requires activating Bax and p53 pathways in TRAIL-resistant lung cancers.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 14;8(11):18095-18105. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14994. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28178647 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic antitumor interaction between valproic acid, capecitabine and radiotherapy in colorectal cancer: critical role of p53.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 6;36(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0647-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29212503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sandler AB, Nemunaitis J, Denham C et al. Phase III trial of gemcitabine plus cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 122–30. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Dancy J, Ramlau R et al. Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive care in patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum‐based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 2095–103. - PubMed
-
- Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non‐small‐cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 1589–97. - PubMed
-
- Shephered FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T et al. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib in previously treated non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 123–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

