Lactate-dehydrogenase 5 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with the expression of the transketolase-like protein 1
- PMID: 20385008
- PMCID: PMC2861018
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-5-22
Lactate-dehydrogenase 5 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with the expression of the transketolase-like protein 1
Abstract
Aims: As one of the five lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) isoenzymes, LDH5 has the highest efficiency to catalyze pyruvate transformation to lactate. LDH5 overexpression in cancer cells induces an upregulated glycolytic metabolism and reduced dependence on the presence of oxygen. Here we analyzed LDH5 protein expression in a well characterized large cohort of primary lung cancers in correlation to clinico-pathological data and its possible impact on patient survival.
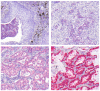
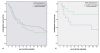
Methods: Primary lung cancers (n = 269) and non neoplastic lung tissue (n = 35) were tested for LDH5 expression by immunohistochemistry using a polyclonal LDH5 antibody (ab53010). The results of LDH5 expression were correlated to clinico-pathological data as well as to patient's survival. In addition, the results of the previously tested transketolase like 1 protein (TKTL1) expression were correlated to LDH5 expression.
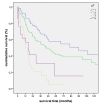
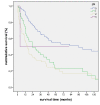
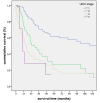
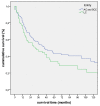
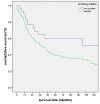
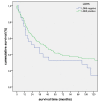
Results: 89.5% (n = 238) of NSCLC revealed LDH5 expression whereas LDH5 expression was not detected in non neoplastic lung tissues (n = 34) (p < 0.0001). LDH5 overexpression was associated with histological type (adenocarcinoma = 57%, squamous cell carcinoma = 45%, large cell carcinoma = 46%, p = 0.006). No significant correlation could be detected with regard to TNM-stage, grading or survival. A two sided correlation between the expression of TKTL1 and LDH5 could be shown (p = 0.002) within the overall cohort as well as for each grading and pN group. A significant correlation between LDH5 and TKTL1 within each histologic tumortype could not be revealed.
Conclusions: LDH5 is overexpressed in NSCLC and could hence serve as an additional marker for malignancy. Furthermore, LDH5 correlates positively with the prognostic marker TKTL1. Our results confirm a close link between the two metabolic enzymes and indicate an alteration in the glucose metabolism in the process of malignant transformation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poor outcome in primary non-small cell lung cancers is predicted by transketolase TKTL1 expression.Pathology. 2011 Dec;43(7):719-24. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0b013e32834c352b. Pathology. 2011. PMID: 22027741
-
Lactate dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) overexpression in non-small-cell lung cancer tissues is linked to tumour hypoxia, angiogenic factor production and poor prognosis.Br J Cancer. 2003 Sep 1;89(5):877-85. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601205. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12942121 Free PMC article.
-
Increased LDH5 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and outcome in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013 Apr;30(4):529-40. doi: 10.1007/s10585-012-9557-2. Epub 2012 Nov 25. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013. PMID: 23184277
-
[Non-small cell lung cancer. New biomarkers for diagnostics and therapy].Pathologe. 2015 Nov;36 Suppl 2:189-93. doi: 10.1007/s00292-015-0084-1. Pathologe. 2015. PMID: 26391246 Review. German.
-
Higher pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase concentration predicts worse overall survival in patients with lung cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(38):e12524. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012524. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30235773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TKTL1 expression in human malign and benign cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2015 Jun 10;15:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-15-2. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26187043 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism and clinical significance of LDHA in HER2-mediated progression of gastric cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Jul 15;10(7):2055-2067. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30093943 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate Contribution to the Tumor Microenvironment: Mechanisms, Effects on Immune Cells and Therapeutic Relevance.Front Immunol. 2016 Feb 16;7:52. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00052. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26909082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Key Amino Acid Residues Surrounding the Active Center of Lactate Dehydrogenase A for the Development of Ideal Inhibitors.Molecules. 2024 Apr 28;29(9):2029. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092029. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731521 Free PMC article.
-
Lactate dehydrogenase A: A key player in carcinogenesis and potential target in cancer therapy.Cancer Med. 2018 Dec;7(12):6124-6136. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1820. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30403008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Warburg O, Posener K, Negelein E. Über den Stoffwechsel der Carcinomzelle. Biochem Z. 1924;152:309–344.
-
- Coy JF, Dressler D, Wilde J, Schubert P. Mutations in the transketolase-like gene TKTL1: clinical implications for neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes and cancer. Clinical laboratory. 2005;51:257–273. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

