The archaeo-eukaryotic GINS proteins and the archaeal primase catalytic subunit PriS share a common domain
- PMID: 20385010
- PMCID: PMC2861644
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-17
The archaeo-eukaryotic GINS proteins and the archaeal primase catalytic subunit PriS share a common domain
Abstract
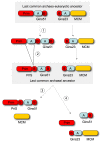
Primase and GINS are essential factors for chromosomal DNA replication in eukaryotic and archaeal cells. Here we describe a previously undetected relationship between the C-terminal domain of the catalytic subunit (PriS) of archaeal primase and the B-domains of the archaeo-eukaryotic GINS proteins in the form of a conserved structural domain comprising a three-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet adjacent to an alpha-helix and a two-stranded beta-sheet or hairpin. The presence of a shared domain in archaeal PriS and GINS proteins, the genes for which are often found adjacent on the chromosome, suggests simple mechanisms for the evolution of these proteins.
Reviewers: This article was reviewed by Zvi Kelman (nominated by Michael Galperin) and Kira Makarova.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A primase subunit essential for efficient primer synthesis by an archaeal eukaryotic-type primase.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 22;6:7300. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8300. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26095544 Free PMC article.
-
A highly divergent archaeo-eukaryotic primase from the Thermococcus nautilus plasmid, pTN2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(6):3707-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1385. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24445805 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis for the subunit assembly of the primase from an archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii.FEBS J. 2007 Mar;274(5):1340-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05690.x. Epub 2007 Feb 5. FEBS J. 2007. PMID: 17286576
-
The Pol α-primase complex.Subcell Biochem. 2012;62:157-69. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4572-8_9. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22918585 Review.
-
The promiscuous primase.Trends Genet. 2005 Oct;21(10):568-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2005.07.010. Trends Genet. 2005. PMID: 16095750 Review.
Cited by
-
The GINS complex from the thermophilic archaeon, Thermoplasma acidophilum may function as a homotetramer in DNA replication.Extremophiles. 2011 Jul;15(4):529-39. doi: 10.1007/s00792-011-0383-2. Epub 2011 Jun 9. Extremophiles. 2011. PMID: 21656171
-
The complete genome sequence of Thermoproteus tenax: a physiologically versatile member of the Crenarchaeota.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e24222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024222. Epub 2011 Oct 7. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22003381 Free PMC article.
-
Architectures of archaeal GINS complexes, essential DNA replication initiation factors.BMC Biol. 2011 Apr 28;9:28. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-9-28. BMC Biol. 2011. PMID: 21527023 Free PMC article.
-
hPrimpol1/CCDC111 is a human DNA primase-polymerase required for the maintenance of genome integrity.EMBO Rep. 2013 Dec;14(12):1104-12. doi: 10.1038/embor.2013.159. Epub 2013 Oct 15. EMBO Rep. 2013. PMID: 24126761 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity purification of an archaeal DNA replication protein network.mBio. 2010 Oct 26;1(5):e00221-10. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00221-10. mBio. 2010. PMID: 20978540 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

