Differential down-regulation of HLA-DR on monocyte subpopulations during systemic inflammation
- PMID: 20385017
- PMCID: PMC2887183
- DOI: 10.1186/cc8959
Differential down-regulation of HLA-DR on monocyte subpopulations during systemic inflammation
Abstract
Introduction: Decreased expression of human leukocyte antigen class II (HLA-DR) on monocytes is a hallmark of altered immune status in patients with a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). So far, the analyses were mainly performed without taking into account monocytes subpopulations.
Methods: We studied this modification on CD14HIGH and CD14LOW monocytes of 20 SIRS patients undergoing abdominal aortic surgery (AAS), 20 patients undergoing carotid artery surgery (CAS), and 9 healthy controls, and we investigated mediators and intracellular molecules that may be involved in this process.
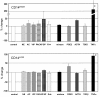
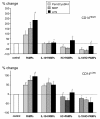
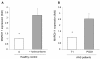
Results: HLA-DR on CD14HIGH monocytes started to decrease during surgery, after blood reperfusion, and was further reduced post-surgery. In contrast, HLA-DR expression on CD14LOW cells only decreased after surgery, and to a lesser extent than on CD14HIGH monocytes. Negative correlations were found between the reduction of HLA-DR expression and the change in cortisol levels for both subpopulations, whereas a negative correlation between interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels and HLA-DR modulation was only observed for CD14HIGH cells. In accordance with these ex vivo results, HLA-DR on CD14HIGH and CD14LOW monocytes of healthy donors was reduced following incubation with hydrocortisone, whereas IL-10 only acted on CD14HIGH subpopulation. Furthermore, flow cytometry revealed that the expression of IL-10 receptor was higher on CD14HIGH versus CD14LOW monocytes. In addition, hydrocortisone, and to a lesser extent IL-10, reversed the up-regulation of HLA-DR induced by bacterial products. Finally, membrane-associated RING-CH-1 protein (MARCH1) mRNA, a negative regulator of MHC class II, was up-regulated in monocytes of AAS patients on Day 1 post-surgery, and in those of healthy subjects exposed to hydrocortisone.
Conclusions: This study reveals that HLA-DR expression is modulated differently on CD14HIGH (classical) versus CD14LOW (inflammatory) monocytes after systemic inflammation.
Figures


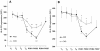
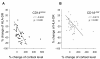
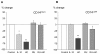

References
-
- Adib-Conquy M, Cavaillon JM. Compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 2009;101:36–47. - PubMed
-
- Venet F, Chung CS, Kherouf H, Geeraert A, Malcus C, Poitevin F, Bohe J, Lepape A, Ayala A, Monneret G. Increased circulating regulatory T cells (CD4(+)CD25 (+)CD127 (-)) contribute to lymphocyte anergy in septic shock patients. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:678–686. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1337-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

