MyD88-dependent and independent pathways of Toll-Like Receptors are engaged in biological activity of Triptolide in ligand-stimulated macrophages
- PMID: 20385024
- PMCID: PMC2873377
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6769-10-3
MyD88-dependent and independent pathways of Toll-Like Receptors are engaged in biological activity of Triptolide in ligand-stimulated macrophages
Abstract
Background: Triptolide is a diterpene triepoxide from the Chinese medicinal plant Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F., with known anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive and anti-cancer properties.
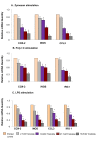
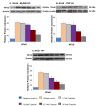
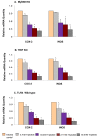
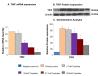
Results: Here we report the expression profile of immune signaling genes modulated by triptolide in LPS induced mouse macrophages. In an array study triptolide treatment modulated expression of 22.5% of one hundred and ninety five immune signaling genes that included Toll-like receptors (TLRs). TLRs elicit immune responses through their coupling with intracellular adaptor molecules, MyD88 and TRIF. Although it is known that triptolide inhibits NFkappaB activation and other signaling pathways downstream of TLRs, involvement of TLR cascade in triptolide activity was not reported. In this study, we show that triptolide suppresses expression of proinflammatory downstream effectors induced specifically by different TLR agonists. Also, the suppressive effect of triptolide on TLR-induced NFkappaB activation was observed when either MyD88 or TRIF was knocked out, confirming that both MyD88 and TRIF mediated NFkappaB activation may be inhibited by triptolide. Within the TLR cascade triptolide downregulates TLR4 and TRIF proteins.
Conclusions: This study reveals involvement of TLR signaling in triptolide activity and further increases understanding of how triptolide activity may downregulate NFkappaB activation during inflammatory conditions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific inhibition of MyD88-independent signaling pathways of TLR3 and TLR4 by resveratrol: molecular targets are TBK1 and RIP1 in TRIF complex.J Immunol. 2005 Sep 1;175(5):3339-46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.3339. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16116226
-
Cinnamaldehyde suppresses toll-like receptor 4 activation mediated through the inhibition of receptor oligomerization.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Jan 15;75(2):494-502. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.08.033. Epub 2007 Sep 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17920563
-
Signaling of apoptosis through TLRs critically involves toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta, but not MyD88, in bacteria-infected murine macrophages.J Immunol. 2004 Sep 1;173(5):3320-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.3320. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15322195
-
Modulation of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor mediated signaling.J Mol Med (Berl). 2005 Apr;83(4):258-66. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0622-4. Epub 2005 Jan 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15662540 Review.
-
Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of triptolide, the principal active diterpenoid from the Chinese medicinal herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f.Drugs R D. 2003;4(1):1-18. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304010-00001. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 12568630 Review.
Cited by
-
A pseudopterane diterpene isolated from the octocoral Pseudopterogorgia acerosa inhibits the inflammatory response mediated by TLR-ligands and TNF-alpha in macrophages.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 16;8(12):e84107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084107. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24358331 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide prevents osteoarthritis via inhibiting hsa-miR-20b.Inflammopharmacology. 2019 Feb;27(1):109-119. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0509-6. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 29974310
-
Tripterygium polyglycosid attenuates the established airway inflammation in asthmatic mice.Chin J Integr Med. 2013 Apr;19(4):282-8. doi: 10.1007/s11655-013-1410-1. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Chin J Integr Med. 2013. PMID: 23321997
-
Triptolide-mediated inhibition of interferon signaling enhances vesicular stomatitis virus-based oncolysis.Mol Ther. 2013 Nov;21(11):2043-53. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.187. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23985699 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin fragment-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases is mediated by MyD88-dependent TLR-2 signaling pathway in human chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Nov 12;17:320. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0833-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26563875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michelsen KS, Wong MH, Shah PK, Zhang W, Yano J, Doherty TM, Akira S, Rajavashisth TB, Arditi M. Lack of Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:10679–10684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403249101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bjorkbacka H, Kunjathoor VV, Moore KJ, Koehn S, Ordija CM, Lee MA, Means T, Halmen K, Luster AD, Golenbock DT, Freeman MW. Reduced atherosclerosis in MyD88-null mice links elevated serum cholesterol levels to activation of innate immunity signaling pathways. Nat Med. 2004;10:416–421. doi: 10.1038/nm1008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2007;Chapter 14(Unit 14):12. - PubMed
-
- Foster SL, Hargreaves DC, Medzhitov R. Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin modifications. Nature. 2007;447:972–978. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

