Transcriptional up-regulation of SOD1 by CEBPD: a potential target for cisplatin resistant human urothelial carcinoma cells
- PMID: 20385105
- PMCID: PMC3586239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.04.007
Transcriptional up-regulation of SOD1 by CEBPD: a potential target for cisplatin resistant human urothelial carcinoma cells
Abstract
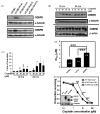
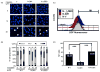
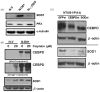
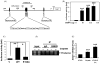
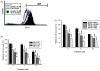
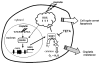
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common type of cancer in men (ninth in women) in the United States. Cisplatin is an effective agent against the most common subtype, urothelial carcinoma. However, the development of chemotherapy resistance is a severe clinical problem for the successful treatment of this and other cancers. A better understanding of the cellular and molecular events in response to cisplatin treatment and the development of resistance are critical to improve the therapeutic options for patients. Here, we report that expression of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (CEBPD, C/EBPdelta, NF-IL6beta) is induced by cisplatin in the human bladder urothelial carcinoma NTUB1 cell line and is specifically elevated in a cisplatin resistant subline. Expression of CEBPD reduced cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis in NTUB1 cells by inducing the expression of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) via direct promoter transactivation. Several reports have implicated CEBPD as a tumor suppressor gene. This study reveals a novel role for CEBPD in conferring drug resistance, suggesting that it can also be pro-oncogenic. Furthermore, our data suggest that SOD inhibitors, which are already used as anti-angiogenic agents, may be suitable for combinatorial chemotherapy to prevent or treat cisplatin resistance in bladder and possibly other cancers.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Bischoff CJ, Clark PE. Bladder cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2009;21:272–7. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman DS. Challenges in the treatment of bladder cancer. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(Suppl 5):v106–12. - PubMed
-
- Bellmunt J, Albiol S, Suarez C, Albanell J. Optimizing therapeutic strategies in advanced bladder cancer: update on chemotherapy and the role of targeted agents. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2009;69:211–22. - PubMed
-
- Zamble DB, Lippard SJ. Cisplatin and DNA repair in cancer chemotherapy. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:435–9. - PubMed
-
- Sedletska Y, Giraud-Panis MJ, Malinge JM. Cisplatin is a DNA-damaging anti-tumour compound triggering multifactorial biochemical responses in cancer cells: importance of apoptotic pathways. Curr Med Chem. 2005;5:251–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

