An in vitro assay system for studying synapse formation between nociceptive dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn neurons
- PMID: 20385165
- PMCID: PMC2880384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.04.002
An in vitro assay system for studying synapse formation between nociceptive dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn neurons
Abstract
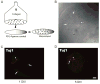
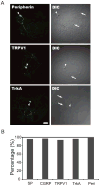
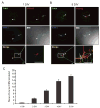
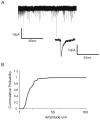
Synapses between nociceptive dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and spinal cord dorsal horn neurons represent the first loci for transmission of painful stimuli. Our knowledge of the molecular organization and development of these synapses is sparse due, partly, to a lack of a reliable model system that reconstitutes synaptogenesis between these two neuronal populations. To address this issue, we have established an in vitro assay system consisting of separately purified DRG neurons and dorsal horn neurons on astrocyte microislands. Using immunocytochemistry, we have found that 97%, 93%, 98%, 96%, and 94% of DRG neurons on these microislands express markers often associated with nociceptive neurons including Substance P, TRPV1, calcitonin-gene related peptide (CGRP), TrKA, and peripherin, respectively. Triple labeling with these nociceptive-like markers, synaptic vesicle marker Vglut2 and using MAP2 as a dendritic marker revealed the presence of nociceptive-like markers at synaptic terminals. Using this immunocytochemical approach, we counted contact points as overlapping MAP2/Vglut2 puncta and showed that they increased with time in culture. Single and dual patch-clamp recordings showed that overlapping Vglut2/MAP2 puncta observed after a few days in culture are likely to be functional synapses between DRG and dorsal horn neurons in our in vitro assay system. Taken together, these data suggest our co-culture microisland model system consists of mostly nociceptive-like DRG neurons that express presynaptic markers and form functional synapses with their dorsal horn partners. Thus, this model system may have direct application for studies on factors regulating development of nociceptive DRG/dorsal horn synapses.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic pregabalin inhibits synaptic transmission between rat dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn neurons in culture.Channels (Austin). 2012 Mar-Apr;6(2):124-32. doi: 10.4161/chan.19805. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Channels (Austin). 2012. PMID: 22627148 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic kainate receptors regulate spinal sensory transmission.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 1;21(1):59-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00059.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11150320 Free PMC article.
-
A two-compartment in vitro model for studies of modulation of nociceptive transmission.J Neurosci Methods. 2001 Feb 15;105(2):175-84. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0270(00)00360-5. J Neurosci Methods. 2001. PMID: 11275274
-
[Pre- and postsynaptic expression mechanisms of long-term depression in rats glutamatergic primary afferent synapses on dorsal horn spinal cord neurons in co-culture].Fiziol Zh (1994). 2013;59(1):117-23. Fiziol Zh (1994). 2013. PMID: 23713358 Ukrainian.
-
[Characteristics of sensory neurotransmission in co-culture of neurons from the dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn spinal cord in rats].Fiziol Zh (1994). 2010;56(4):26-36. Fiziol Zh (1994). 2010. PMID: 20968035 Ukrainian.
Cited by
-
Localization of the Priming Factors CAPS1 and CAPS2 in Mouse Sensory Neurons Is Determined by Their N-Termini.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Apr 14;15:674243. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.674243. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35493323 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neurite outgrowth by activation of calcium-permeable kainate receptors expressed by rat nociceptive-like dorsal root ganglion neurons.Dev Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;71(10):818-35. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20906. Dev Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21557511 Free PMC article.
-
The EGF-LIKE domain of thrombospondin-4 is a key determinant in the development of pain states due to increased excitatory synaptogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 19;293(42):16453-16463. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003591. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30194282 Free PMC article.
-
Paralogs of the Calcium-Dependent Activator Protein for Secretion Differentially Regulate Synaptic Transmission and Peptide Secretion in Sensory Neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep 11;12:304. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00304. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30254567 Free PMC article.
-
A microfluidic model of the first sensory synapse for analgesic target discovery.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241293286. doi: 10.1177/17448069241293286. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 39415077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albuquerque C, Lee CJ, Jackson AC, MacDermott AB. Subpopulations of GABAergic and non-GABAergic rat dorsal horn neurons express Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2758–2766. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque C, Joseph DJ, Choudhury P, MacDermott AB. Preparation of coverslips for neuronal cultures. CSH Protoc. 2009 Aug 1;2009(8) pdb.prot5272. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque C, Joseph DJ, Choudhury P, MacDermott AB. Dissection, plating, and maintenance of cortical astrocyte cultures. CSH Protoc. 2009 Aug 1;2009(8) pdb.prot5273. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque C, Joseph DJ, Choudhury P, MacDermott AB. Dissection, plating, and maintenance of dorsal horn neuron cultures. CSH Protoc. 2009 Aug 1;2009(8) pdb.prot5274. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque C, Joseph DJ, Choudhury P, MacDermott AB. Dissection, Plating and maintenance of dissociated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons for mono-culture and for co-culture with dorsal horn neurons. CSH Protoc. 2009 Aug 1;2009(8) pdb.prot5275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

