Variants of contextual fear conditioning are differentially impaired in the juvenile rat by binge ethanol exposure on postnatal days 4-9
- PMID: 20385174
- PMCID: PMC3918449
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.04.003
Variants of contextual fear conditioning are differentially impaired in the juvenile rat by binge ethanol exposure on postnatal days 4-9
Abstract
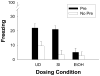
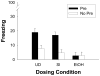
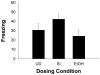
Neonatal ethanol exposure in the rat is known to partially damage the hippocampus, but such exposure causes only modest or inconsistent deficits on hippocampus-dependent behavioral tasks. This may reflect variable sensitivity of these tasks or residual function following partial hippocampal injury. The context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE) is a variant of context conditioning in which context exposure and immediate shock occur on successive occasions. During testing, preexposed rats freeze more than non-preexposed controls. The CPFE is more sensitive to anterograde hippocampal injury than standard contextual fear conditioning (e.g., Rudy JW, O'Reilly RC. Conjunctive representations, the hippocampus, and contextual fear conditioning. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2001;1:66-82). We report that rats exposed to a high binge dose of ethanol (5.25g/kg/day) over postnatal days [PD] 4-9 failed to demonstrate the CPFE when preexposed to the conditioning context on PD31, relative to sham-intubated and undisturbed controls (Experiment 1). Neonatal alcohol disrupted conditioned freezing to a much lesser extent relative to controls when context preexposure was followed by a standard context conditioning trial rather than immediate shock (Experiment 2). Fear conditioning to a discrete auditory cue (tone) was unaffected by neonatal alcohol exposure ruling out possible performance effects (Experiment 3). These findings suggest that the CPFE is an especially sensitive task for detecting hippocampal injury produced by neonatal alcohol. Mixed results with other tasks may reflect residual hippocampal function and/or the use of alternate neurobehavioral systems or "strategies" following alcohol-induced brain damage.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of dose and period of neonatal alcohol exposure on the context preexposure facilitation effect.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Jun;35(6):1160-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01449.x. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21352243 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal alcohol exposure and the hippocampus in developing male rats: effects on behaviorally induced CA1 c-Fos expression, CA1 pyramidal cell number, and contextual fear conditioning.Neuroscience. 2012 Mar 29;206:89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22285885 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal alcohol impairs the context preexposure facilitation effect in juvenile rats: dose-response and post-training consolidation effects.Alcohol. 2014 Feb;48(1):35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Alcohol. 2014. PMID: 24387902 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal ethanol exposure impairs long-term context memory formation and prefrontal immediate early gene expression in adolescent rats.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Feb 1;359:386-395. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30447241 Free PMC article.
-
Consequences of ethanol exposure on cued and contextual fear conditioning and extinction differ depending on timing of exposure during adolescence or adulthood.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Nov 1;256:10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.08.013. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23938333 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Differential expression of the immediate early genes c-Fos, Arc, Egr-1, and Npas4 during long-term memory formation in the context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE).Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Jan;147:128-138. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29222058 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise and environmental complexity on deficits in trace and contextual fear conditioning produced by neonatal alcohol exposure in rats.Dev Psychobiol. 2013 Jul;55(5):483-95. doi: 10.1002/dev.21052. Epub 2012 May 29. Dev Psychobiol. 2013. PMID: 22644967 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of postnatal alcohol exposure and galantamine on the context pre-exposure facilitation effect and acetylcholine efflux using in vivo microdialysis.Alcohol. 2015 May;49(3):193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.01.010. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25837482 Free PMC article.
-
Egr-1 mRNA expression patterns in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala during variants of contextual fear conditioning in adolescent rats.Brain Res. 2014 Aug 12;1576:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.06.007. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24976583 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Run: Neuroprotective Effects of Physical Exercise on Adult Neurogenesis from Youth to Old Age.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017;15(4):519-533. doi: 10.2174/1570159X14666160412150223. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27000776 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abel EL, Sokol RJ. Fetal alcohol syndrome is now leading cause of mental retardation. Lancet. 1986;2:1222. - PubMed
-
- Allan AM, Chynoweth J, Tyler LA, Caldwell KK. A mouse model of prenatal ethanol exposure using a voluntary drinking paradigm. Alcoholism-Clinical and Experimental Research. 2003;27:2009–2016. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Gale GD, Fanselow MS. Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus. 2001;11:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, O’Reilly RC, Rudy JW. Memory for context is impaired by injecting anisomycin into dorsal hippocampus following context exploration. Behav Brain Res. 2002;134:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

