Aging attenuates radiation-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in rat brain
- PMID: 20385203
- PMCID: PMC2875775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.04.009
Aging attenuates radiation-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in rat brain
Abstract
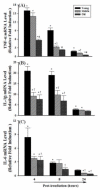
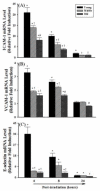
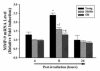
The present study was designed to examine the effect of aging on radiation-induced expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in rat brain. Male F344xBN rats (4, 16, and 24 months of age) received either whole brain irradiation with a single dose of 10Gy gamma-rays or sham-irradiation, and were maintained for 4, 8, and 24h post-irradiation. The mRNA expression levels of various pro-inflammatory mediators such as cytokines, adhesion molecules, chemokine, and matrix metalloproteinase were analyzed by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The acute inflammatory responses to irradiation, including overexpression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), interleukin-6 (IL-6), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), E-selectin, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) were markedly attenuated in the hippocampus of middle-aged and old rats compared with young groups. Specifically, a significant age-dependent decrease in TNF-alpha expression was detected 8 and 24h after irradiation and a similar age-related attenuation was observed in IL-1beta, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 expression 4 and 8h post-irradiation. MCP-1 expression was reduced 4h post-irradiation and MMP-9 expression at 8h post-irradiation. These results provide evidence for the first time that radiation-induced pro-inflammatory responses in the brain are suppressed in aged animals.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2000;21:383–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akwa Y, Hassett DE, Eloranta ML, Sandberg K, Masliah E, Powell H, Whitton JL, Bloom FE, C m ampbell IL. Transgenic expression of IFN-alpha in the central nervous system of mice protects against lethal neurotropic viral infection but induces inflammation and neurodegeneration. J. Immunol. 1998;161:5016–5026. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft GS, Horan MA, Ferguson MW. Aging alters the inflammatory and endothelial cell adhesion molecule profiles during human cutaneous wound healing. Lab. Invest. 1998;78:47–58. - PubMed
-
- Caruso C, Candore G, Cigna D, DiLorenzo G, Sireci G, Dieli F, Salerno A. Cytokine production pathway in the elderly. Immunol. Res. 1996;15:84–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

