Unique bell-shaped voltage-dependent modulation of Na+ channel gating by novel insect-selective toxins from the spider Agelena orientalis
- PMID: 20385552
- PMCID: PMC2881780
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125211
Unique bell-shaped voltage-dependent modulation of Na+ channel gating by novel insect-selective toxins from the spider Agelena orientalis
Abstract
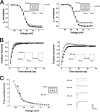
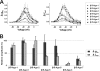
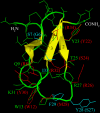
Spider venoms provide a highly valuable source of peptide toxins that act on a wide diversity of membrane-bound receptors and ion channels. In this work, we report isolation, biochemical analysis, and pharmacological characterization of a novel family of spider peptide toxins, designated beta/delta-agatoxins. These toxins consist of 36-38 amino acid residues and originate from the venom of the agelenid funnel-web spider Agelena orientalis. The presented toxins show considerable amino acid sequence similarity to other known toxins such as mu-agatoxins, curtatoxins, and delta-palutoxins-IT from the related spiders Agelenopsis aperta, Hololena curta, and Paracoelotes luctuosus. beta/delta-Agatoxins modulate the insect Na(V) channel (DmNa(V)1/tipE) in a unique manner, with both the activation and inactivation processes being affected. The voltage dependence of activation is shifted toward more hyperpolarized potentials (analogous to site 4 toxins) and a non-inactivating persistent Na(+) current is induced (site 3-like action). Interestingly, both effects take place in a voltage-dependent manner, producing a bell-shaped curve between -80 and 0 mV, and they are absent in mammalian Na(V) channels. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first detailed report of peptide toxins with such a peculiar pharmacological behavior, clearly indicating that traditional classification of toxins according to their binding sites may not be as exclusive as previously assumed.
Figures




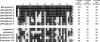
References
-
- Estrada G., Villegas E., Corzo G. (2007) Nat. Prod. Rep. 24, 145–161 - PubMed
-
- Grishin E. (1999) Eur. J. Biochem. 264, 276–280 - PubMed
-
- Rash L. D., Hodgson W. C. (2002) Toxicon 40, 225–254 - PubMed
-
- Vassilevski A. A., Kozlov S. A., Grishin E. V. (2009) Biochemistry 74, 1505–1534 - PubMed
-
- Catterall W. A. (2000) Neuron 26, 13–25 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

