NUDT16 is a (deoxy)inosine diphosphatase, and its deficiency induces accumulation of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA and growth arrest
- PMID: 20385596
- PMCID: PMC2919730
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq249
NUDT16 is a (deoxy)inosine diphosphatase, and its deficiency induces accumulation of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA and growth arrest
Abstract
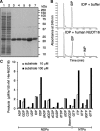
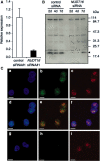
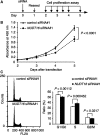
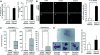
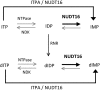
Nucleotides function in a variety of biological reactions; however, they can undergo various chemical modifications. Such modified nucleotides may be toxic to cells if not eliminated from the nucleotide pools. We performed a screen for modified-nucleotide binding proteins and identified human nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X-type motif 16 (NUDT16) protein as an inosine triphosphate (ITP)/xanthosine triphosphate (XTP)/GTP-binding protein. Recombinant NUDT16 hydrolyzes purine nucleoside diphosphates to the corresponding nucleoside monophosphates. Among 29 nucleotides examined, the highest k(cat)/K(m) values were for inosine diphosphate (IDP) and deoxyinosine diphosphate (dIDP). Moreover, NUDT16 moderately hydrolyzes (deoxy)inosine triphosphate ([d]ITP). NUDT16 is mostly localized in the nucleus, and especially in the nucleolus. Knockdown of NUDT16 in HeLa MR cells caused cell cycle arrest in S-phase, reduced cell proliferation, increased accumulation of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA as well as increased levels of inosine in RNA. We thus concluded that NUDT16 is a (deoxy)inosine diphosphatase that may function mainly in the nucleus to protect cells from deleterious effects of (d)ITP.
Figures

References
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA Repair And Mutagenesis. 2nd edn. Washington: ASM Press; 2005.
-
- Nakabeppu Y, Sakumi K, Sakamoto K, Tsuchimoto D, Tsuzuki T, Nakatsu Y. Mutagenesis and carcinogenesis caused by the oxidation of nucleic acids. Biol. Chem. 2006;387:373–379. - PubMed
-
- Nakabeppu Y, Kajitani K, Sakamoto K, Yamaguchi H, Tsuchimoto D. MTH1, an oxidized purine nucleoside triphosphatase, prevents the cytotoxicity and neurotoxicity of oxidized purine nucleotides. DNA Repair. 2006;5:761–772. - PubMed
-
- Nakabeppu Y, Tsuchimoto D, Yamaguchi H, Sakumi K. Oxidative damage in nucleic acids and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007;85:919–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

