SIRT1 is a redox-sensitive deacetylase that is post-translationally modified by oxidants and carbonyl stress
- PMID: 20385619
- PMCID: PMC2923349
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-151308
SIRT1 is a redox-sensitive deacetylase that is post-translationally modified by oxidants and carbonyl stress
Abstract
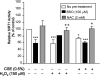
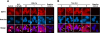
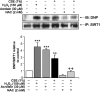
Sirtuin1 (SIRT1) deacetylase levels are decreased in chronic inflammatory conditions and aging where oxidative stress occurs. We determined the mechanism of SIRT1 redox post-translational modifications leading to its degradation. Human lung epithelial cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide (150-250 microM), aldehyde-acrolein (10-30 microM), and cigarette smoke extract (CSE; 0.1-1.5%) in the presence of intracellular glutathione-modulating agents at 1-24 h, and oxidative post-translational modifications were assayed in cells, as well as in lungs of mice lacking and overexpressing glutaredoxin-1 (Glrx1), and wild-type (WT) mice in response to cigarette smoke (CS). CSE and aldehydes dose and time dependently decreased SIRT1 protein levels, with EC(50) of 1% for CSE and 30 microM for acrolein at 6 h, and >80% inhibition at 24 h with CSE, which was regulated by modulation of intracellular thiol status of the cells. CS decreased the lung levels of SIRT1 in WT mice, which was enhanced by deficiency of Glrx1 and prevented by overexpression of Glrx1. Oxidants, aldehydes, and CS induced carbonyl modifications on SIRT1 on cysteine residues concomitant with decreased SIRT1 activity. Proteomics studies revealed alkylation of cysteine residue on SIRT1. Our data suggest that oxidants/aldehydes covalently modify SIRT1, decreasing enzymatic activity and marking the protein for proteasomal degradation, which has implications in inflammatory conditions.
Figures

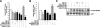
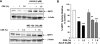



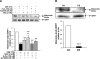

References
-
- Elliott P J, Jirousek M. Sirtuins: novel targets for metabolic disease. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;9:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Westphal C H, Dipp M A, Guarente L. A therapeutic role for sirtuins in diseases of aging? Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:555–560. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Zhou Y, Mueller-Steiner S, Chen L F, Kwon H, Yi S, Mucke L, Gan L. SIRT1 protects against microglia-dependent amyloid-beta toxicity through inhibiting NF-κB signaling. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:40364–40374. - PubMed
-
- Vogelmeier C, Bals R. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and premature aging. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:1217–1218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

