Compound haploinsufficiencies of Ebf1 and Runx1 genes impede B cell lineage progression
- PMID: 20385820
- PMCID: PMC2867885
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003525107
Compound haploinsufficiencies of Ebf1 and Runx1 genes impede B cell lineage progression
Abstract
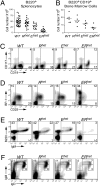
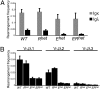
Early B cell factor (EBF)1 is essential for B lineage specification. Previously, we demonstrated the synergistic activation of Cd79a (mb-1) genes by EBF1 and its functional partner, RUNX1. Here, we identified consequences of Ebf1 haploinsufficiency together with haploinsufficiency of Runx1 genes in mice. Although numbers of "committed" pro-B cells were maintained in Ebf1(+/-)Runx1(+/-) (ER(het)) mice, activation of B cell-specific gene transcription was depressed in these cells. Expression of genes encoding Aiolos, kappa0 sterile transcripts, CD2 and CD25 were reduced and delayed in ER(het) pro-B cells, whereas surface expression of BP-1 was increased on late pro-B cells in ER(het) mice. Late pre-B and immature and mature B cells were decreased in the bone marrow of Ebf1(+/-) (E(het)) mice and were nearly absent in ER(het) mice. Although we did not observe significant effects of haploinsuficiencies on IgH or Igkappa rearrangements, a relative lack of Iglambda rearrangements was detected in E(het) and ER(het) pre-B cells. Together, these observations suggest that B cell lineage progression is impaired at multiple stages in the bone marrow of E(het) and ER(het) mice. Furthermore, enforced expression of EBF1 and RUNX1 in terminally differentiated plasmacytoma cells activated multiple early B cell-specific genes synergistically. Collectively, these studies illuminate the effects of reduced Ebf1 dosage and the compounding effects of reduced Runx1 dosage. Our data confirm and extend the importance of EBF1 in regulating target genes and Ig gene rearrangements necessary for B cell lineage specification, developmental progression, and homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nutt SL, Kee BL. The transcriptional regulation of B cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2007;26:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Lin H, Grosschedl R. Failure of B-cell differentiation in mice lacking the transcription factor EBF. Nature. 1995;376:263–267. - PubMed
-
- Medina KL, et al. Assembling a gene regulatory network for specification of the B cell fate. Dev Cell. 2004;7:607–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

