Sustained experience of emotion after loss of memory in patients with amnesia
- PMID: 20385824
- PMCID: PMC2867870
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914054107
Sustained experience of emotion after loss of memory in patients with amnesia
Abstract
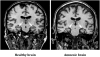
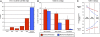
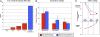
Can the experience of an emotion persist once the memory for what induced the emotion has been forgotten? We capitalized on a rare opportunity to study this question directly using a select group of patients with severe amnesia following circumscribed bilateral damage to the hippocampus. The amnesic patients underwent a sadness induction procedure (using affectively-laden film clips) to ascertain whether their experience of sadness would persist beyond their memory for the sadness-inducing films. The experiment showed that the patients continued to experience elevated levels of sadness well beyond the point in time at which they had lost factual memory for the film clips. A second experiment using a happiness induction procedure yielded similar results, suggesting that both positive and negative emotional experiences can persist independent of explicit memory for the inducing event. These findings provide direct evidence that a feeling of emotion can endure beyond the conscious recollection for the events that initially triggered the emotion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cahill L, Prins B, Weber M, McGaugh JL. β-Adrenergic activation and memory for emotional events. Nature. 1994;371:702–704. - PubMed
-
- Hamann S. Cognitive and neural mechanisms of emotional memory. Trends Cogn Sci. 2001;5:394–400. - PubMed
-
- LaBar KS, Cabeza R. Cognitive neuroscience of emotional memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:54–64. - PubMed
-
- Bower GH. Mood and memory. Am Psychol. 1981;36:129–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

