EGCG remodels mature alpha-synuclein and amyloid-beta fibrils and reduces cellular toxicity
- PMID: 20385841
- PMCID: PMC2867908
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910723107
EGCG remodels mature alpha-synuclein and amyloid-beta fibrils and reduces cellular toxicity
Abstract
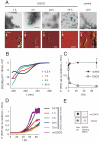
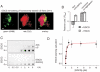
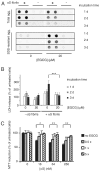
Protein misfolding and formation of beta-sheet-rich amyloid fibrils or aggregates is related to cellular toxicity and decay in various human disorders including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Recently, we demonstrated that the polyphenol (-)-epi-gallocatechine gallate (EGCG) inhibits alpha-synuclein and amyloid-beta fibrillogenesis. It associates with natively unfolded polypeptides and promotes the self-assembly of unstructured oligomers of a new type. Whether EGCG disassembles preformed amyloid fibrils, however, remained unclear. Here, we show that EGCG has the ability to convert large, mature alpha-synuclein and amyloid-beta fibrils into smaller, amorphous protein aggregates that are nontoxic to mammalian cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that the compound directly binds to beta-sheet-rich aggregates and mediates the conformational change without their disassembly into monomers or small diffusible oligomers. These findings suggest that EGCG is a potent remodeling agent of mature amyloid fibrils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhu M, et al. The flavonoid baicalein inhibits fibrillation of alpha-synuclein and disaggregates existing fibrils. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(26):26846–26857. - PubMed
-
- Ehrnhoefer DE, et al. Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin-gallate modulates early events in huntingtin misfolding and reduces toxicity in Huntington’s disease models. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(18):2743–2751. - PubMed
-
- Rambold AS, et al. Green tea extracts interfere with the stress-protective activity of PrP and the formation of PrP. J Neurochem. 2008;107(1):218–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

