Antimicrobial activity of a halocidin-derived peptide resistant to attacks by proteases
- PMID: 20385874
- PMCID: PMC2897289
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01790-09
Antimicrobial activity of a halocidin-derived peptide resistant to attacks by proteases
Abstract
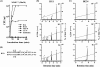
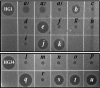
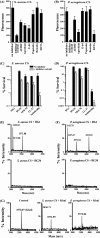
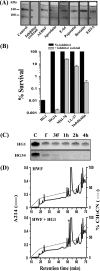
Cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have attracted a great deal of interest as a promising candidate for a novel class of antibiotics that might effectively treat recalcitrant infections caused by a variety of microbes that are resistant to currently available drugs. However, the AMPs are inherently limited in that they are inevitably susceptible to attacks by proteases generated by human and pathogenic microbes; this vulnerability severely hinders their pharmaceutical use in human therapeutic protocols. In this study, we report that a halocidin-derived AMP, designated HG1, was found to be resistant to proteolytic degradation. As a result of its unique structural features, HG1 proved capable of preserving its antimicrobial activity after incubation with trypsin, chymotrypsin, and human matrix metalloprotease 7 (MMP-7). Additionally, HG1 was observed to exhibit profound antimicrobial activity in the presence of fluid from human skin wounds or proteins extracted from the culture supernatants of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Greater understanding of the structural motifs of HG1 required for its protease resistance might provide feasible ways to solve the problems intrinsic to the development of an AMP-based antibiotic.
Figures


References
-
- Batista, C. V., A. Scaloni, D. J. Rigden, L. R. Silva, A. Rodrigues Romero, R. Dukor, A. Sebben, F. Talamo, and C. Bloch. 2001. A novel heterodimeric antimicrobial peptide from the tree-frog Phyllomedusa distincta. FEBS Lett. 494:85-89. - PubMed
-
- Brewer, D., and G. Lajoie. 2002. Structure-based design of potent histatin analogues. Biochemistry 41:5526-5536. - PubMed
-
- Campopiano, D. J., D. J. Clarke, N. C. Polfer, P. E. Barran, R. J. Langley, J. R. Govan, A. Maxwell, and J. R. Dorin. 2004. Structure-activity relationships in defensin dimers: a novel link between beta-defensin tertiary structure and antimicrobial activity. J. Biol. Chem. 279:48671-48679. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2006. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 7th ed. Approved standard M7-A7. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Dalla Serra, M., O. Cirioni, R. M. Vitale, G. Renzone, M. Coraiola, A. Giacometti, C. Potrich, E. Baroni, G. Guella, M. Sanseverino, S. De Luca, G. Scalise, P. Amodeo, and A. Scaloni. 2008. Structural features of distinctin affecting peptide biological and biochemical properties. Biochemistry 47:7888-7899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

