Regulatory (FoxP3+) T-cell tumor infiltration is a favorable prognostic factor in advanced colon cancer patients undergoing chemo or chemoimmunotherapy
- PMID: 20386463
- PMCID: PMC7322625
- DOI: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181d32f01
Regulatory (FoxP3+) T-cell tumor infiltration is a favorable prognostic factor in advanced colon cancer patients undergoing chemo or chemoimmunotherapy
Abstract
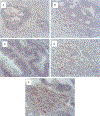
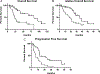
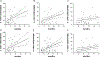
Antitumor immune response and chemotherapy-induced immunomodulation in colon cancer patients represented the rationale to design new strategies, like GOLFIG chemoimmunotherapy (gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil/folinic acid, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and aldesleukine), that resulted a safe and very active regimen. Antitumor activity and immunity feedback to GOLFIG were strictly correlated with the best outcome observed in patients with autoimmunity signs, increase of central memory T cells, and decrease of regulatory T cells (Treg) in the peripheral blood. We thus investigated a potential correlation between the Treg tumor infiltration at diagnosis and the clinical outcome in a current randomized phase 3 trial aimed to compare the GOLFIG regimen with the standard FOLFOX chemotherapy (GOLFIG-2). An immunohistochemistry study was carried out to quantify the infiltration of Treg/FoxP3+ T lymphocytes in tumor samples of 57 patients enrolled in the GOLFIG-2 trial. Treg tumor infiltration scores were correlated with overall survival, treatment-relative survival, and progression-free survival (PFS). Higher Treg tumor infiltration scores were associated with a better prognosis in the whole series (Treg high score vs. low score: overall survival=mean 43.2 mo vs. 28.6 mo, P=0.0005) and a better outcome after treatment (Treg high score vs. low score: PFS=mean 15.8 mo vs. 8.8 mo, P=0.0009; treatment-relative survival=mean 23.1 mo vs. 18.2 mo, P=0.004). PFS was significantly longer in GOLFIG high versus all other subgroups (mean 18.1 mo vs. 9.9 mo, P=0.01). Our results suggest that a higher FoxP3+ T-lymphocyte tumor infiltration score is a favorable prognostic factor in colon cancer patients undergoing chemo or chemoimmunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared there are no financial conflicts of interest in regard to this work.
All the authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide In: GLOBOCAN 2000 version 1.0 IARC CancerBase N Lyon: 5 IARC Press; 2001.
-
- Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RJ. Systemic therapy for colorectalcancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:476–487. - PubMed
-
- Correale P, Campoccia G, Tsang KY, et al. Recruitment of dendritic cells and enhanced antigen specific immune-reactivity in cancer patients treated with hrGMCSF (molgramostim) and hr IL-2: results from a Phase Ib Clinical Trial. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:892–902. - PubMed
-
- Correale P, Cusi MG, Tsang KY, et al. Chemo-immunotherapy of metastatic colorectal carcinoma with gemcitabine plus FOLFOX 4 followed by subcutaneous granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor and interleukin-2 induces strong immunological and antitumor activity in metastatic colon cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8950–8958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

