Dissociation of calmodulin from cardiac ryanodine receptor causes aberrant Ca(2+) release in heart failure
- PMID: 20388639
- PMCID: PMC3025723
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvq108
Dissociation of calmodulin from cardiac ryanodine receptor causes aberrant Ca(2+) release in heart failure
Abstract
Aims: Calmodulin (CaM) is well known to modulate the channel function of the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2). However, the possible role of CaM on the aberrant Ca(2+) release in diseased hearts remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the state of RyR2-bound CaM and channel dysfunctions in pacing-induced failing hearts.
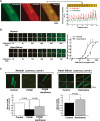
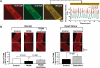
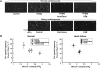
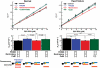
Methods and results: The characteristics of CaM binding to RyR2 and the role of CaM on the aberrant Ca(2+) release were assessed in normal and failing canine hearts. The affinity of CaM binding to RyR2 was lower in failing sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) than in normal SR. Addition of FK506, which dissociates FKBP12.6 from RyR2, to normal SR reduced the CaM-binding affinity. Dantrolene restored a normal level of the CaM-binding affinity in either FK506-treated (normal) SR or failing SR, suggesting that the defective inter-domain interaction between the N-terminal domain and the central domain of RyR2 (the therapeutic target of dantrolene) is involved in the reduction of the CaM-binding affinity in failing hearts. In saponin-permeabilized cardiomyocytes, the frequency of spontaneous Ca(2+) sparks was much more increased in failing cardiomyocytes than in normal cardiomyocytes, whereas the addition of a high concentration of CaM attenuated the aberrant increase of Ca(2+) sparks.
Conclusion: The defective inter-domain interaction between N-terminal and central domains within RyR2 reduces the binding affinity of CaM to RyR2, thereby causing the spontaneous Ca(2+) release events in failing hearts. Correction of the defective CaM binding may be a new strategy to protect against the aberrant Ca(2+) release in heart failure.
Figures

Comment in
-
Calmodulin: a gatekeeper for ryanodine receptor function in the myocardium.Cardiovasc Res. 2010 Sep 1;87(4):587-8. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq215. Epub 2010 Jun 29. Cardiovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20587508 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yano M, Yamamoto T, Ikemoto N, Matsuzaki M. Abnormal ryanodine receptor function in heart failure. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;107:377–391. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.04.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marx SO, Reiken S, Hisamatsu Y, Jayaraman T, Burkhoff D, Rosemblit N, et al. PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell. 2000;101:365–376. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80847-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yano M, Ono K, Ohkusa T, Suetsugu M, Kohno M, Hisaoka T, et al. Altered stoichiometry of FKBP12.6 versus ryanodine receptor as a cause of abnormal Ca2+ leak through ryanodine receptor in heart failure. Circulation. 2000;102:2131–2136. - PubMed
-
- Ai X, Curran JW, Shannon TR, Bers DM, Pogwizd SM. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase modulates cardiac ryanodine receptor phosphorylation and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak in heart failure. Circ Res. 2005;97:1314–1322. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000194329.41863.89. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yano M, Yamamoto T, Ikeda Y, Matsuzaki M. Mechanisms of disease: ryanodine receptor defects in heart failure and fatal arrhythmia. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006;3:43–52. doi:10.1038/ncpcardio0419. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

