Blueberry phytochemicals inhibit growth and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through modulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway
- PMID: 20388778
- PMCID: PMC2862148
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3565
Blueberry phytochemicals inhibit growth and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through modulation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway
Abstract
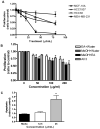
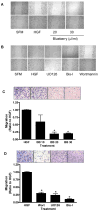
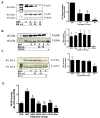
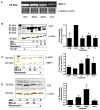
Dietary phytochemicals are known to exhibit a variety of anticarcinogenic properties. This study investigated the chemopreventive activity of blueberry extract in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Blueberry decreased cell proliferation in HCC38, HCC1937, and MDA-MB-231 cells with no effect on the nontumorigenic MCF-10A cell line. Decreased metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells by blueberry was shown through inhibition of cell motility using wound-healing assays and migration through a polyethylene terephthalate membrane. Blueberry treatment decreased the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and the secretion of urokinase-type plasminogen activator while increasing tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 secretion in MDA-MB-231 conditioned medium as shown by Western blotting. Cell signaling pathways that control the expression/activation of these processes were investigated via Western blotting and reporter gene assay. Treatment with blueberry decreased phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and NFkappaB activation in MDA-MB-231 cells, where protein kinase C and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) were not affected. In vivo, the efficacy of blueberry to inhibit triple-negative breast tumor growth was evaluated using the MDA-MB-231 xenograft model. Tumor weight and proliferation (Ki-67 expression) were decreased in blueberry-treated mice, where apoptosis (caspase-3 expression) was increased compared with controls. Immunohistochemical analysis of tumors from blueberry-fed mice showed decreased activation of AKT and p65 NFkappaB signaling proteins with no effect on the phosphorylation of ERK. These data illustrate the inhibitory effect of blueberry phytochemicals on the growth and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells through modulation of the PI3K/AKT/NFkappaB pathway.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008;52:108–18. - PubMed
-
- Cleator S, Heller W, Coombes RC. Triple-negative breast cancer: therapeutic options. The lancet oncology. 2007;8:235–44. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD, Brunet JS, Stefansson IM, et al. The prognostic implication of the basal-like (cyclin E high/p27 low/p53+/glomeruloid-microvascular-proliferation+) phenotype of BRCA1-related breast cancer. Cancer research. 2004;64:830–5. - PubMed
-
- Tsuda H, Takarabe T, Hasegawa F, Fukutomi T, Hirohashi S. Large, central acellular zones indicating myoepithelial tumor differentiation in high-grade invasive ductal carcinomas as markers of predisposition to lung and brain metastases. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2000;24:197–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

