Salmonid genomes have a remarkably expanded akirin family, coexpressed with genes from conserved pathways governing skeletal muscle growth and catabolism
- PMID: 20388840
- PMCID: PMC2888561
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00045.2010
Salmonid genomes have a remarkably expanded akirin family, coexpressed with genes from conserved pathways governing skeletal muscle growth and catabolism
Abstract
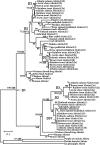
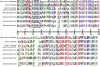
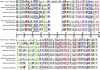
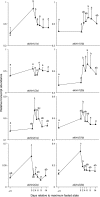
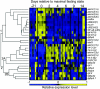
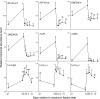
Metazoan akirin genes regulate innate immunity, myogenesis, and carcinogenesis. Invertebrates typically have one family member, while most tetrapod and teleost vertebrates have one to three. We demonstrate an expanded repertoire of eight family members in genomes of four salmonid fishes, owing to paralog preservation after three tetraploidization events. Retention of paralogs secondarily lost in other teleosts may be related to functional diversification and posttranslational regulation. We hypothesized that salmonid akirins would be transcriptionally regulated in fast-twitch skeletal muscle during activation of conserved pathways governing catabolism and growth. The in vivo nutritional state of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus L.) was experimentally manipulated, and transcript levels for akirin family members and 26 other genes were measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR), allowing the establishment of a similarity network of expression profiles. In fasted muscle, a class of akirins was upregulated, with one family member showing high coexpression with catabolic genes coding the NF-kappaB p65 subunit, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, E3 ubiquitin ligases, and IGF-I receptors. Another class of akirin was upregulated with subsequent feeding, coexpressed with 14-3-3 protein genes. There was no similarity between expression profiles of akirins with IGF hormones or binding protein genes. The level of phylogenetic relatedness of akirin family members was not a strong predictor of transcriptional responses to nutritional state, or differences in transcript abundance levels, indicating a complex pattern of regulatory evolution. The salmonid akirins epitomize the complexity linking the genome to physiological phenotypes of vertebrates with a history of tetraploidization.
Figures
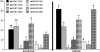
References
-
- Abascal F, Zardoya R, Posada D. ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 21: 2104–2105, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Aguilera C, Fernández-Majada V, Inglés-Esteve J, Rodilla V, Bigas A, Espinosa L. Efficient nuclear export of p65-IkappaBalpha complexes requires 14-3-3 proteins. J Cell Sci 119: 3695–3704, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Allendorf FW, Thorgaard GH. Tetraploidy and the evolution of salmonid fishes. In: Evolutionary Genetics of Fishes, edited by Turner BJ. New York: Plenum, 1984
-
- Andersen CL, Ledet-Jensen J, Ørntoft T. Normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64: 5245–5250, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

