Crosstalk between insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and G protein-coupled receptor signaling systems: a novel target for the antidiabetic drug metformin in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 20388847
- PMCID: PMC2862089
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2229
Crosstalk between insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors and G protein-coupled receptor signaling systems: a novel target for the antidiabetic drug metformin in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
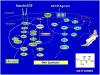
Insulin/insulin-like growth factor 1(IGF-1) receptors and G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) signaling systems are implicated in autocrine-paracrine stimulation of a variety of malignancies, including ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, one of the most lethal human diseases. Novel targets for pancreatic cancer therapy are urgently needed. We identified a crosstalk between insulin/IGF-1 receptors and GPCR signaling systems in pancreatic cancer cells, leading to enhanced signaling, DNA synthesis, and proliferation. Crosstalk between these signaling systems depends on mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 (mTORC1). Metformin, the most widely used drug in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, activates AMP kinase (AMPK), which negatively regulates mTORC1. Recent results show that metformin-induced activation of AMPK disrupts crosstalk between insulin/IGF-1 receptor and GPCR signaling in pancreatic cancer cells and inhibits the growth of these cells in xenograft models. Given that insulin/IGF-1 and GPCRs are implicated in other malignancies, a similar crosstalk mechanism may be operative in other cancer cell types. Recent epidemiological studies linked administration of metformin with a reduced risk of pancreatic, breast, and prostate cancer in diabetic patients. We posit that crosstalk between insulin/IGF-1 receptor and GPCR signaling is a mechanism for promoting the development of certain types of cancer and a target for the prevention and therapy of these diseases via metformin administration.
Copyright 2010 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Rozengurt E. Mitogenic signaling pathways induced by G protein-coupled receptors. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:589–602. - PubMed
-
- Kisfalvi K, Rey O, Young SH, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E. Insulin Potentiates Ca2+ Signaling and Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate Hydrolysis Induced by Gq Protein-Coupled Receptor Agonists through an mTOR-Dependent Pathway. Endocrinology. 2007;148:3246–57. - PubMed
-
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986;234:161–6. - PubMed
-
- Dorsam RT, Gutkind JS. G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:79–94. - PubMed
-
- Ryder NM, Guha S, Hines OJ, Reber HA, Rozengurt E. G protein-coupled receptor signaling in human ductal pancreatic cancer cells: Neurotensin responsiveness and mitogenic stimulation. J Cell Physiol. 2001;186:53–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

