Non-redundant roles for LXRalpha and LXRbeta in atherosclerosis susceptibility in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 20388921
- PMCID: PMC2853457
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M900096
Non-redundant roles for LXRalpha and LXRbeta in atherosclerosis susceptibility in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice
Abstract
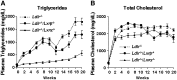
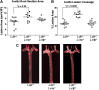
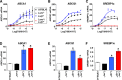
The liver X receptors LXRalpha and LXRbeta play critical roles in maintaining lipid homeostasis by functioning as transcription factors that regulate genetic networks controlling the transport, catabolism, and excretion of cholesterol. The studies described in this report examine the individual anti-atherogenic activity of LXRalpha and LXRbeta and determine the ability of each subtype to mediate the biological response to LXR agonists. Utilizing individual knockouts of LXRalpha and LXRbeta in the Ldlr(-/-) background, we demonstrate that LXRalpha has a dominant role in limiting atherosclerosis in vivo. Functional studies in macrophages indicate that LXRalpha is required for a robust response to LXR ligands, whereas LXRbeta functions more strongly as a repressor. Furthermore, selective knockout of LXRalpha in hematopoietic cells and rescue experiments indicate that the anti-atherogenic activity of this LXR subtype is not restricted to macrophages. These studies indicate that LXRalpha plays a selective role in limiting atherosclerosis in response to hyperlipidemia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Liver LXRα expression is crucial for whole body cholesterol homeostasis and reverse cholesterol transport in mice.J Clin Invest. 2012 May;122(5):1688-99. doi: 10.1172/JCI59817. Epub 2012 Apr 9. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22484817 Free PMC article.
-
LXRalpha regulates human CETP expression in vitro and in transgenic mice.Atherosclerosis. 2010 Sep;212(1):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.04.025. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Atherosclerosis. 2010. PMID: 20494359
-
Knock-down of the oxysterol receptor LXRα impairs cholesterol efflux in human primary macrophages: lack of compensation by LXRβ activation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Jul 1;86(1):122-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.12.024. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23313547
-
Liver X receptors as potential therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis.Clin Invest Med. 2009 Oct 1;32(5):E383-94. doi: 10.25011/cim.v32i5.6927. Clin Invest Med. 2009. PMID: 19796580 Review.
-
Liver X receptor: a potential target in the treatment of atherosclerosis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022 Jul;26(7):645-658. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2117610. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022. PMID: 36003057 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Roles of Liver X Receptors in Lipid Metabolism and Immunity in Atherosclerosis.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 14;15(4):579. doi: 10.3390/biom15040579. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver x receptors in atherosclerosis and inflammation.Circ Res. 2011 Apr 15;108(8):996-1001. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.226878. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21493922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic polarization of macrophages in atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jun;33(6):1120-6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300173. Epub 2013 May 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23640492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation Triggers Liver X Receptor-Dependent Lipogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jan 3;40(2):e00364-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00364-19. Print 2020 Jan 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31658997 Free PMC article.
-
LXR ligands induce apoptosis of EGFR-TKI-resistant human lung cancer cells in vitro by inhibiting Akt-NF-κB activation.Oncol Lett. 2018 May;15(5):7168-7174. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8182. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29731879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glass C. K., Witztum J. L. 2001. Atherosclerosis. The road ahead. Cell. 104: 503–516. - PubMed
-
- Tontonoz P., Mangelsdorf D. J. 2003. Liver X receptor signaling pathways in cardiovascular disease. Mol. Endocrinol. 17: 985–993. - PubMed
-
- Costet P., Luo Y., Wang N., Tall A. R. 2000. Sterol-dependent transactivation of the ABC1 promoter by the liver X receptor/retinoid X receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 28240–28245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

