Caveolins sequester FA on the cytoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane, augment triglyceride formation, and protect cells from lipotoxicity
- PMID: 20388923
- PMCID: PMC2853459
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M900251
Caveolins sequester FA on the cytoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane, augment triglyceride formation, and protect cells from lipotoxicity
Abstract
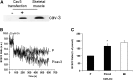
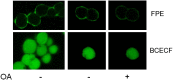
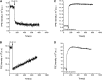
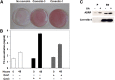
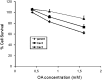
Ectopic expression of caveolin-1 in HEK293 cells enhances FA sequestration in membranes as measured by a pH-sensitive fluorescent dye (1). We hypothesized that sequestration of FA is due to the enrichment of caveolin in the cytosolic leaflet and its ability to facilitate the formation of lipid rafts to buffer high FA levels. Here we show that ec-topic expression of caveolin-3 also results in enhanced FA sequestration. To further discriminate the effect that caveolins have on transmembrane FA movement and distribution, we labeled the outer membrane leaflet with fluorescein-phosphatidylethanolamine (FPE), whose emission is quenched by the presence of FA anions. Real-time measurements made with FPE and control experiments with positively charged fatty amines support our hypothesis that caveolins promote localization of FA anions through interactions with basic amino acid residues (lysines and arginines) present at the C termini of caveolins-1 and -3.
Figures
References
-
- Meshulam T., Simard J. R., Wharton J., Hamilton J. A., Pilch P. F. 2006. Role of caveolin-1 and cholesterol in transmembrane fatty acid movement. Biochemistry. 45: 2882–2893. (PubMed). - PubMed
-
- Parton R. G., Simons K. 2007. The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8: 185–194. (PubMed). - PubMed
-
- Spisni E., Tomasi V., Cestaro A., Tosatto S. C. 2005. Structural insights into the function of human caveolin 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 338: 1383–1390. (PubMed). - PubMed
-
- Dietzen D. J., Hastings W. R., Lublin D. M. 1995. Caveolin is palmitoylated on multiple cysteine residues. Palmitoylation is not necessary for localization of caveolin to caveolae. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 6838–6842. (PubMed). - PubMed
-
- Monier S., Dietzen D. J., Hastings W. R., Lublin D. M., Kurzchalia T. V. 1996. Oligomerization of VIP21-caveolin in vitro is stabilized by long chain fatty acylation or cholesterol. FEBS Lett. 388: 143–149. (PubMed). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

