Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism near the interleukin-28B gene with response to hepatitis C therapy in HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients
- PMID: 20389235
- PMCID: PMC4892373
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283391d6d
Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism near the interleukin-28B gene with response to hepatitis C therapy in HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients
Abstract
Background: Given that peginterferon-ribavirin treatment is poorly tolerated, there is interest in the identification of predictors of response, particularly in HIV/hepatitis C virus (HCV)-coinfected patients that respond less than HCV-monoinfected individuals. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) near the IL28B gene (rs12979860) has been shown to predict treatment response in HCV-monoinfected patients carrying genotype 1. Information is lacking for HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals and/or other HCV genotypes.
Methods: From 650 HIV/HCV-coinfected patients, we identified those who had completed a course of peginterferon-ribavirin therapy with a validated outcome and available repository DNA. The rs12979860 SNP was examined in a blinded fashion.
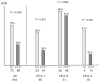
Results: A total of 164 patients were included in the final IL28B genotyping analysis, 90 (55%) of whom achieved sustained virological response (SVR). HCV genotype distribution was as follows: HCV-1 58%, HCV-3 31% and HCV-4 11%. Overall, the SVR rate was higher in patients with CC than in those CT/TT genotypes: 56 of 75 (75%) versus 34 of 89 (38%) (P < 0.0001). The effect of the SNP was seen in HCV genotypes 1 and 4 but not in HCV genotype 3 carriers. In the multivariable analysis (odds ratio; 95% confidence interval; P value), the rs12979860 CC genotype was a strong predictor of SVR (3.7; 1.6-8.5; 0.002), independent of HCV genotype 3 (8.0; 3.1-21.0; <0.001), serum HCV-RNA less than 600,000 IU/ml (11.9; 3.8-37.4; <0.001) and lack of advanced liver fibrosis (3.5; 1.4-8.9; 0.009).
Conclusion: The rs12979860 SNP located near the IL28B gene is associated with HCV treatment response in HIV-infected patients with chronic hepatitis C due to genotypes 1 or 4. Thus, IL28B genotyping should be considered as part of the treatment decision algorithm in this difficult-to-treat population.
Figures
References
-
- Lauer G, Walker B. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:41–52. - PubMed
-
- Soriano V, Puoti M, Sulkowski M, Cargnel A, Benhamou Y, Peters M, et al. Care of patients coinfected with HIV and hepatitis C virus: 2007 updated recommendations from the HCV-HIV International Panel. AIDS. 2007;21:1073–1089. - PubMed
-
- Graham C, Baden L, Yu E, Mrus J, Carnie J, Heeren T, et al. Influence of HIV infection on the course of hepatitis C virus infection: a meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:562–569. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Carbonero L, Benhamou Y, Puoti M, Berenguer J, Mallolas J, Quereda C, et al. Incidence and predictors of severe liver fibrosis in HIV-infected patients with chronic hepatitis C: a European collaborative study. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:128–133. - PubMed
-
- Weber R, Sabin C, Friis-Møller N, Reiss P, El-Sadr W, Kirk O, et al. Liver-related deaths in persons infected with the HIV: the D:A:D study. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1632–1641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases