High speed optical coherence microscopy with autofocus adjustment and a miniaturized endoscopic imaging probe
- PMID: 20389435
- PMCID: PMC2908909
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.18.004222
High speed optical coherence microscopy with autofocus adjustment and a miniaturized endoscopic imaging probe
Abstract
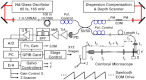
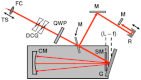
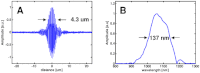
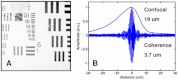
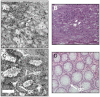
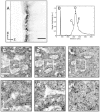
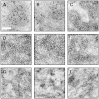
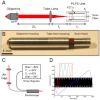
Optical coherence microscopy (OCM) is a promising technique for high resolution cellular imaging in human tissues. An OCM system for high-speed en face cellular resolution imaging was developed at 1060 nm wavelength at frame rates up to 5 Hz with resolutions of < 4 microm axial and < 2 microm transverse. The system utilized a novel polarization compensation method to combat wavelength dependent source polarization and achieve broadband electro-optic phase modulation compatible with ultrahigh axial resolution. In addition, the system incorporated an auto-focusing feature that enables precise, near real-time alignment of the confocal and coherence gates in tissue, allowing user-friendly optimization of image quality during the imaging procedure. Ex vivo cellular images of human esophagus, colon, and cervix as well as in vivo results from human skin are presented. Finally, the system design is demonstrated with a miniaturized piezoelectric fiber-scanning probe which can be adapted for laparoscopic and endoscopic imaging applications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Miniaturized precalibration-based Lissajous scanning fiber probe for high speed endoscopic optical coherence tomography.Opt Lett. 2020 Apr 15;45(8):2470-2473. doi: 10.1364/OL.389364. Opt Lett. 2020. PMID: 32287261
-
Micromotor endoscope catheter for in vivo, ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography.Opt Lett. 2004 Oct 1;29(19):2261-3. doi: 10.1364/ol.29.002261. Opt Lett. 2004. PMID: 15524374
-
Ultrahigh speed spectral-domain optical coherence microscopy.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Jul 1;4(8):1236-54. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001236. eCollection 2013. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 24009989 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography.J Biomed Opt. 2004 Jan-Feb;9(1):47-74. doi: 10.1117/1.1629679. J Biomed Opt. 2004. PMID: 14715057 Review.
-
Point-of-care pathology with miniature microscopes.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2011;34(3):81-98. doi: 10.3233/ACP-2011-011. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21673433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correction of coherence gate curvature in high numerical aperture optical coherence imaging.Opt Lett. 2010 Sep 15;35(18):3120-2. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.003120. Opt Lett. 2010. PMID: 20847798 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a handheld optical coherence microscopy endoscope.J Biomed Opt. 2011 Jun;16(6):066018. doi: 10.1117/1.3594149. J Biomed Opt. 2011. PMID: 21721819 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh speed en face OCT capsule for endoscopic imaging.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 Mar 5;6(4):1146-63. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.001146. eCollection 2015 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 25909001 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in situ cellular imaging full-field optical coherence tomography with a rigid endoscopic probe.Biomed Opt Express. 2011 Oct 1;2(10):2897-904. doi: 10.1364/BOE.2.002897. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Biomed Opt Express. 2011. PMID: 22025991 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh speed endoscopic optical coherence tomography using micromotor imaging catheter and VCSEL technology.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Jun 14;4(7):1119-32. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001119. Print 2013 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 23847737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kempe M., Rudolph W., Welsch E., “Comparative study of confocal and heterodyne microscopy for imaging through scattering media,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 13(1), 46–52 (1996).10.1364/JOSAA.13.000046 - DOI
-
- Izatt J. A., Kulkarni M. D., Wang H.-W., Kobayashi K., Sivak M. V., Jr, “Optical coherence tomography and microscopy in gastrointestinal tissues,” IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quan. Electron. 2(4), 1017–1028 (1996).10.1109/2944.577331 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

