Discovery of brain-penetrant, orally bioavailable aminothienopyridazine inhibitors of tau aggregation
- PMID: 20392114
- PMCID: PMC2872922
- DOI: 10.1021/jm100138f
Discovery of brain-penetrant, orally bioavailable aminothienopyridazine inhibitors of tau aggregation
Abstract
Agents capable of preventing the misfolding and sequestration of the microtubule-stabilizing protein tau into insoluble fibrillar aggregates hold considerable promise for the prevention and/or treatment of neurodegenerative tauopathies such as Alzheimer's disease. Because tauopathies are characterized by amyloidosis that is restricted to the central nervous system (CNS), plausible candidate compounds for in vivo evaluation must both prevent tau fibrillization and achieve significant brain levels. Recently, we reported the discovery of the aminothienopyridazine (ATPZ) class of tau aggregation inhibitors and now describe a series of new analogues that are both effective inhibitors of tau fibrillization and display significant brain-to-plasma exposure ratios after administration to mice. Further, two of the most promising examples, 15 and 16, were found to reach significant brain exposure levels following oral administration. Taken together, these results suggest that examples from the ATPZ class hold promise as candidates for in vivo efficacy studies in animal models of neurodegenerative tauopathies.
Figures





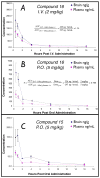

References
-
- Lee VMY, Goedert M, Trojanowski JQ. Neurodegenerative Tauopathies. Ann Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1121–1159. - PubMed
-
- Mazanetz MP, Fischer PM. Untangling tau hyperphosphorylation in drug design for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:464–479. - PubMed
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VMY, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

