Estimated risk of perihippocampal disease progression after hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy: safety profile for RTOG 0933
- PMID: 20392503
- PMCID: PMC2981132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.02.030
Estimated risk of perihippocampal disease progression after hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy: safety profile for RTOG 0933
Abstract
Background and purpose: RTOG 0933 is a phase II clinical trial of hippocampal avoidance during whole-brain radiotherapy (HA-WBRT) to prevent radiation-induced neurocognitive decline. By quantifying baseline incidence of perihippocampal or hippocampal metastasis, we sought to estimate the risk of developing metastases in the hippocampal avoidance region (the hippocampus plus 5mm margin).
Materials/methods: Patients with < or = 10 brain metastases treated at two separate institutions were reviewed. Axial images from pre-treatment, post-contrast MRIs were used to contour each metastasis and hippocampus according to a published protocol. Clinical and radiographic variables were correlated with perihippocampal metastasis using a binary logistical regression analysis, with two-sided p<0.05 for statistical significance.
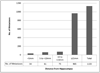
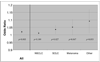
Results: 1133 metastases were identified in 371 patients. Metastases within 5mm of the hippocampus were observed in 8.6% of patients (95% CI 5.7-11.5%) and 3.0% of brain metastases. None of the metastases lay within the hippocampus. A 1-cm(3) increase in the aggregate volume of intra-cranial metastatic disease was associated with an odds ratio of 1.02 (95% CI 1.006-1.034, p=0.003) for the presence of perihippocampal metastasis.
Conclusion: With an estimated perihippocampal metastasis risk of 8.6%, we deem HA-WBRT safe for clinical testing in patients with brain metastases as part of RTOG 0933.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Notification: None
Figures

Comment in
-
The distribution of brain metastases in the perihippocampal region (Regarding Gondi et al., Radiother Oncol 2010;95:327-331).Radiother Oncol. 2011 Jan;98(1):144. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.11.004. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Radiother Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21159399 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Incidence of hippocampal and perihippocampal brain metastases and impact on hippocampal-avoiding radiotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Radiother Oncol. 2024 Aug;197:110331. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110331. Epub 2024 May 19. Radiother Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38772476
-
Quality assurance analysis of hippocampal avoidance in a melanoma whole brain radiotherapy randomized trial shows good compliance.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Jul 20;13(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-1077-z. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30029684 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Is Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Risky for Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer? Hippocampal Metastasis Rate and Associated Risk Factors.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Dec;16(6):1202-1208. doi: 10.1177/1533034617742301. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 29332467 Free PMC article.
-
Perihippocampal failure after hippocampal-avoidance brain radiotherapy in small cell lung cancer patients: Cases report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 12;103(28):e38884. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038884. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38996135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perihippocampal failure after hippocampal-avoidance whole-brain radiotherapy in cancer patients with brain metastases: Results of a retrospective analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Apr 8;101(14):e29144. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029144. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35446298 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Whole-brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on metastases: neurocognitive testing and biological imaging (HIPPORAD) - a phase II prospective randomized multicenter trial (NOA-14, ARO 2015-3, DKTK-ROG).BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 8;20(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07011-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32513138 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer in the era of immunotherapy: pathological complete response to neoadjuvant pembrolizumab and chemotherapy.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Oct;9(5):2059-2073. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-896. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33209626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Different Head Tilt Angles in Tomotherapy and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241281326. doi: 10.1177/15330338241281326. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39233627 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of high‑risk factors for brain metastasis and prognosis after prophylactic cranial irradiation in limited‑stage small cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jul 3;28(3):422. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14555. eCollection 2024 Sep. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39035048 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic melanoma to the brain: surgery and radiation is still the standard of care.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2013 Jun;14(2):264-79. doi: 10.1007/s11864-013-0228-6. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23504304
References
-
- Mehta MP, Rodrigus P, Terhaard CH, et al. Survival and neurologic outcomes in a randomized trial of motexafin gadolinium and whole-brain radiation therapy in brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2529–2536. - PubMed
-
- Mehta MP, Shapiro WR, Glantz MJ, et al. Lead-in phase to randomized trial of motexafin gadolinium and whole-brain radiation for patients with brain metastases: centralized assessment of magnetic resonance imaging, neurocognitive, and neurologic end points. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3445–3453. - PubMed
-
- Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;37:745–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

