Reconstruction of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the breast with temporal constraints
- PMID: 20392585
- PMCID: PMC2900842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.001
Reconstruction of dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the breast with temporal constraints
Abstract
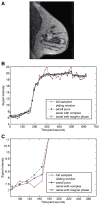
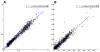
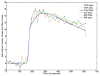
A number of methods using temporal and spatial constraints have been proposed for reconstruction of undersampled dynamic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. The complex data can be constrained or regularized in a number of different ways, for example, the time derivative of the magnitude and phase image voxels can be constrained separately or jointly. Intuitively, the performance of different regularizations will depend on both the data and the chosen temporal constraints. Here, a complex temporal total variation (TV) constraint was compared to the use of separate real and imaginary constraints, and to a magnitude constraint alone. Projection onto Convex Sets (POCS) with a gradient descent method was used to implement the diverse temporal constraints in reconstructions of DCE MRI data. For breast DCE data, serial POCS with separate real and imaginary TV constraints was found to give relatively poor results while serial/parallel POCS with a complex temporal TV constraint and serial POCS with a magnitude-only temporal TV constraint performed well with an acceleration factor as large as R=6. In the tumor area, the best method was found to be parallel POCS with complex temporal TV constraint. This method resulted in estimates for the pharmacokinetic parameters that were linearly correlated to those estimated from the fully-sampled data, with K(trans,R=6)=0.97 K(trans,R=1)+0.00 with correlation coefficient r=0.98, k(ep,R=6)=0.95 k(ep,R=1)+0.00 (r=0.85). These results suggest that it is possible to acquire highly undersampled breast DCE-MRI data with improved spatial and/or temporal resolution with minimal loss of image quality.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancement-constrained acceleration: A robust reconstruction framework in breast DCE-MRI.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 28;16(10):e0258621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258621. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34710110 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive k-space sampling design for edge-enhanced DCE-MRI using compressed sensing.Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Sep;32(7):899-912. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2013.12.022. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24848294
-
Iterative projection onto convex sets for quantitative susceptibility mapping.Magn Reson Med. 2015 Feb;73(2):697-703. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25155. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Magn Reson Med. 2015. PMID: 24604410 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MR imaging.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009 May;17(2):351-62. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2009.01.010. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009. PMID: 19406363 Review.
-
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of breast cancer.J Am Coll Radiol. 2009 Jul;6(7):523-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2009.04.006. J Am Coll Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19560072 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Myocardial perfusion MRI with an undersampled 3D stack-of-stars sequence.Med Phys. 2012 Aug;39(8):5204-11. doi: 10.1118/1.4738965. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22894445 Free PMC article.
-
A feasible high spatiotemporal resolution breast DCE-MRI protocol for clinical settings.Magn Reson Imaging. 2012 Nov;30(9):1257-67. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.04.009. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22770687 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated Brain DCE-MRI Using Iterative Reconstruction With Total Generalized Variation Penalty for Quantitative Pharmacokinetic Analysis: A Feasibility Study.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Aug;16(4):446-460. doi: 10.1177/1533034616649294. Epub 2016 May 23. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 27215931 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of compressed sensing in quantitative MR imaging of cancer.Cancer Imaging. 2013 Dec 30;13(4):633-44. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2013.0041. Cancer Imaging. 2013. PMID: 24434808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Location constrained approximate message passing for compressed sensing MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2013 Aug;70(2):370-81. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24468. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Magn Reson Med. 2013. PMID: 23042658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madore B, Glover GH, Pelc NJ. Unaliasing by Fourier-encoding the Overlaps using the temporaL Dimension (UNFOLD), applied to cardiac imaging and fMRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42(5):813–28. - PubMed
-
- van Vaals JJ, Brummer ME, Dixon WT, Tuithof HH, Engels H, Nelson RC, et al. “Keyhole” method for accelerating imaging of contrast agent uptake. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1993;3(4):671–5. - PubMed
-
- Webb AG, Liang ZP, Magin RL, Lauterbur PC. Applications of reduced-encoding MR imaging with generalized-series reconstruction (RIGR) J Magn Reson Imaging. 1993;3(6):925–8. - PubMed
-
- Tsao J, Boesigner P, Pruessmann KP. k-t BLAST and k-t SENSE: dynamic MRI with high frame rate exploiting spatiotemporal correlations. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50(5):1031–42. - PubMed
-
- Jung H, Sung K, Nayak KS, Kim EY, Ye JC. k-t FOCUSS: a general compressed sensing framework for high resolution dynamic MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61(1):103–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

