Metabolic actions of insulin in men and women
- PMID: 20392600
- PMCID: PMC2893237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nut.2009.10.013
Metabolic actions of insulin in men and women
Abstract
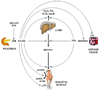
Insulin is an important regulator of glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism. It suppresses hepatic glucose and triglyceride production, inhibits adipose tissue lipolysis and whole-body and muscle proteolysis, and stimulates glucose uptake in muscle. In this review we discuss what is currently known about the control of substrate metabolism by insulin in men and women. The data available so far indicate that women are more sensitive to insulin with regards to glucose metabolism (both in the liver and in muscle), whereas there are no differences between men and women in insulin action on lipolysis. Potential differences exist in the regulation of plasma triglyceride concentration and protein metabolism by insulin and in changes in insulin action in response to stimuli (e.g., weight loss and exercise) that are known to alter insulin sensitivity. However, these areas have not been studied comprehensively enough to draw firm conclusions.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Lafontan M, Langin D. Lipolysis and lipid mobilization in human adipose tissue. Prog Lipid Res. 2009;48:275–297. - PubMed
-
- Jensen MD, Caruso M, Heiling V, Miles JM. Insulin regulation of lipolysis in nondiabetic and IDDM subjects. Diabetes. 1989;38:1595–1601. - PubMed
-
- Lewis GF, Uffelman KD, Szeto LW, Steiner G. Effects of acute hyperinsulinemia on VLDL triglyceride and VLDL apoB production in normal weight and obese individuals. Diabetes. 1993;42:833–842. - PubMed
-
- Lewis GF, Zinman B, Uffelman KD, Szeto L, Weller B, Steiner G. VLDL production is decreased to a similar extent by acute portal vs. peripheral venous insulin. Am J Physiol. 1994;267:E566–E572. - PubMed
-
- Mead JR, Irvine SA, Ramji DP. Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J Mol Med. 2002;80:753–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AR 49869/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG031297/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HD 057796/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR024994/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK 56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG 031297/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG031297/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD057796/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR049869/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

