New roles for cyclin E in megakaryocytic polyploidization
- PMID: 20392692
- PMCID: PMC2881813
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102145
New roles for cyclin E in megakaryocytic polyploidization
Abstract
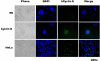
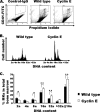
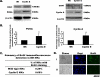
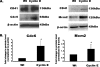
Megakaryocytes are platelet precursor cells that undergo endomitosis. During this process, repeated rounds of DNA synthesis are characterized by lack of late anaphase and cytokinesis. Physiologically, the majority of the polyploid megakaryocytes in the bone marrow are cell cycle arrested. As previously reported, cyclin E is essential for megakaryocyte polyploidy; however, it has remained unclear whether up-regulated cyclin E is an inducer of polyploidy in vivo. We found that cyclin E is up-regulated upon stimulation of primary megakaryocytes by thrombopoietin. Transgenic mice in which elevated cyclin E expression is targeted to megakaryocytes display an increased ploidy profile. Examination of S phase markers, specifically proliferating cell nuclear antigen, cyclin A, and 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine reveals that cyclin E promotes progression to S phase and cell cycling. Interestingly, analysis of Cdc6 and Mcm2 indicates that cyclin E mediates its effect by promoting the expression of components of the pre-replication complex. Furthermore, we show that up-regulated cyclin E results in the up-regulation of cyclin B1 levels, suggesting an additional mechanism of cyclin E-mediated ploidy increase. These findings define a key role for cyclin E in promoting megakaryocyte entry into S phase and hence, increase in the number of cell cycling cells and in augmenting polyploidization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The cell cycle in polyploid megakaryocytes is associated with reduced activity of cyclin B1-dependent cdc2 kinase.J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 23;271(8):4266-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.8.4266. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8626773
-
Overexpression of cyclin D1 in the Dami megakaryocytic cell line causes growth arrest.Blood. 1995 Jul 1;86(1):294-304. Blood. 1995. PMID: 7795236
-
Overexpression of cyclin D1 moderately increases ploidy in megakaryocytes.Haematologica. 2001 Jan;86(1):17-23. Haematologica. 2001. PMID: 11146565
-
Cyclins and cell division kinases in megakaryocytic endomitosis.C R Acad Sci III. 1995 Jun;318(6):649-54. C R Acad Sci III. 1995. PMID: 7671009 Review.
-
Roads to polyploidy: the megakaryocyte example.J Cell Physiol. 2002 Jan;190(1):7-20. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10035. J Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11807806 Review.
Cited by
-
BMP2K dysregulation promotes abnormal megakaryopoiesis in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia.Cell Biosci. 2020 Apr 15;10:57. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00418-y. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32322386 Free PMC article.
-
Polyploidy in tissue homeostasis and regeneration.Development. 2018 Jul 18;145(14):dev156034. doi: 10.1242/dev.156034. Development. 2018. PMID: 30021843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidases and reactive oxygen species during hematopoiesis: a focus on megakaryocytes.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Oct;227(10):3355-62. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24071. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22331622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronan Depolymerization by Megakaryocyte Hyaluronidase-2 Is Required for Thrombopoiesis.Am J Pathol. 2016 Sep;186(9):2390-403. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.05.004. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27398974 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Cycle Re-entry in the Nervous System: From Polyploidy to Neurodegeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 24;9:698661. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.698661. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34249947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balduini C. L., Savoia A. (2004) Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 30, 513–523 - PubMed
-
- Ravid K., Lu J., Zimmet J. M., Jones M. R. (2002) J. Cell. Physiol. 190, 7–20 - PubMed
-
- Kaushansky K., Drachman J. G. (2002) Oncogene 21, 3359–3367 - PubMed
-
- Deutsch V. R., Tomer A. (2006) Br. J. Haematol. 134, 453–466 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

