Choline promotes nicotinic receptor alpha4 + beta2 up-regulation
- PMID: 20392695
- PMCID: PMC2888390
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.108803
Choline promotes nicotinic receptor alpha4 + beta2 up-regulation
Abstract
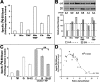
Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) composed of alpha4 + beta2 subunits, the high affinity nicotine-binding site in the mammalian brain, up-regulate in response to chronic nicotine exposure. The identities of endogenous mediators of this process are unknown. We find that choline also up-regulates alpha4 + beta2 nAChRs stably expressed by HEK293 cells as measured by increased [(3)H]epibatidine density. Choline-mediated up-regulation is dose-dependent and corresponds with an increase in beta2 subunit protein expression. The choline kinase inhibitor hemicholinium-3 inhibits approximately 60% of choline-mediated up-regulation revealing both an HC3-dependent and -independent pathway. Furthermore, choline-mediated up-regulation is not additive with up-regulation agents such as nicotine, but it is additive with weaker promoters of the up-regulation process. When co-applied with the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha, choline-mediated up-regulation is increased further through a mechanism that includes an increase in both alpha4 and beta2 protein expression, and this is inhibited by the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190. These findings extend the view that up-regulation of alpha4 + beta2 nAChRs is a normal physiological response to altered metabolic and inflammatory conditions.
Figures
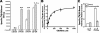


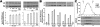
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

