Expression of ammonia transporter family members, Rh B glycoprotein and Rh C glycoprotein, in the developing rat kidney
- PMID: 20392801
- PMCID: PMC2904167
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00607.2009
Expression of ammonia transporter family members, Rh B glycoprotein and Rh C glycoprotein, in the developing rat kidney
Abstract
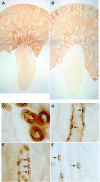
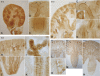
Ammonia metabolism is a primary component of acid-base homeostasis but is incompletely developed at time of birth. Rh B glycoprotein (Rhbg) and Rh C glycoprotein (Rhcg) are recently recognized ammonia transporter family members expressed in the mammalian kidney. This study's purpose was to establish the expression and localization of Rhbg and Rhcg during kidney development. We examined kidneys from fetal days 16 (E16), 18 (E18), and 20 (E20), and from the first 21 days of postnatal development. Rhbg was expressed initially at E18, with expression only in the connecting tubule (CNT); at E20, Rhbg was expressed in both the CNT and the medullary collecting duct (MCD). In contrast, Rhcg was first expressed at E16 with basal expression in the ureteric bud; at E18, it was expressed in a subset of CNT cells with an apical pattern, followed by apical and basolateral expression in the MCD at E20. In the cortex, Rhbg and Rhcg expression increased in the CNT before expression in the cortical collecting duct during fetal development. In the MCD, both Rhbg and Rhcg expression was initially in cells in the papillary tip, with gradual removal from the tip during the late fetal period and transition during the early neonatal period to an adult pattern with predominant expression in the outer MCD and only rare expression in cells in the initial inner MCD. Double-labeling with intercalated cell-specific markers identified that Rhbg and Rhcg were expressed initially in CNT cells, CNT A-type intercalated cells and non-A, non-B intercalated cells, and in MCD A-type intercalated cells. We conclude that expression of Rhbg and Rhcg parallels intercalated cell development and that immature Rhbg and Rhcg expression at birth contributes to incomplete ammonia excretion capacity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Localization of the ammonium transporter proteins RhBG and RhCG in mouse kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Feb;284(2):F323-37. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00050.2002. Epub 2002 Oct 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12388412
-
Renal and hepatic expression of the ammonium transporter proteins, Rh B Glycoprotein and Rh C Glycoprotein.Acta Physiol Scand. 2003 Dec;179(4):331-8. doi: 10.1046/j.0001-6772.2003.01210.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003. PMID: 14656370 Review.
-
RhBG and RhCG, the putative ammonia transporters, are expressed in the same cells in the distal nephron.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003 Mar;14(3):545-54. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000050413.43662.55. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 12595489
-
Renal expression of the ammonia transporters, Rhbg and Rhcg, in response to chronic metabolic acidosis.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F397-408. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00162.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16144966
-
Molecular physiology of the Rh ammonia transport proteins.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010 Sep;19(5):471-7. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32833bfa4e. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2010. PMID: 20539225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of hypokalemia on renal expression of the ammonia transporter family members, Rh B Glycoprotein and Rh C Glycoprotein, in the rat kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Oct;301(4):F823-32. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00266.2011. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21753075 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficiency of the ammonia transporter Rhcg predisposes to chronic acidosis: Rhcg is critical for apical and basolateral ammonia transport in the mouse collecting duct.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 22;288(8):5518-29. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.441782. Epub 2012 Dec 31. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23281477 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the ammonia transporter family member, Rh B Glycoprotein, in the human kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Apr 1;304(7):F972-81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00550.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23324176 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intercalated cell-specific Rh C glycoprotein deletion on basal and metabolic acidosis-stimulated renal ammonia excretion.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Aug;299(2):F369-79. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00120.2010. Epub 2010 May 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20462967 Free PMC article.
-
Role of NH3 and NH4+ transporters in renal acid-base transport.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Jan;300(1):F11-23. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00554.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21048022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benyajati S, Goldstein L. Renal glutaminase adaptation and ammonia excretion in infant rats. Am J Physiol 228: 693–698, 1975 - PubMed
-
- Biver S, Belge H, Bourgeois S, Van Vooren P, Nowik M, Scohy S, Houillier P, Szpirer J, Szpirer C, Wagner CA, Devuyst O, Marini AM. A role for Rhesus factor Rhcg in renal ammonium excretion and male fertility. Nature 456: 339–343, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bonnici B, Wagner CA. Postnatal expression of transport proteins involved in acid-base transport in mouse kidney. Pflügers Arch 448: 16–28, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

