Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a mediates mammary ductal branching and proliferation in the nulliparous mouse
- PMID: 20392833
- PMCID: PMC2875824
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1282
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a mediates mammary ductal branching and proliferation in the nulliparous mouse
Abstract
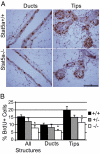
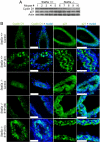
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat)5a is a critical regulator of mammary gland development. Previous studies have focused on Stat5a's role in the late pregnant and lactating gland, and although active Stat5a is detectable in mammary epithelial cells in virgin mice, little is known about its role during early mammary gland development. In this report, we compare mammary gland morphology in pubertal and adult nulliparous wild-type and Stat5a-/- mice. The Stat5a-null mammary glands exhibited defects in secondary and side branching, providing evidence that Stat5a regulates these processes. In addition, Stat5a-/- mammary glands displayed an attenuated proliferative response to pregnancy levels of estrogen plus progesterone (E+P), suggesting that it plays an important role in early pregnancy. Finally, we examined one potential mediator of Stat5a's effects, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL). Stat5a-/- mammary glands were defective in inducing RANKL in response to E+P treatment. In addition, regulation of several reported RANKL targets, including inhibitor of DNA binding 2 (Id2), cyclin D1, and the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Waf1/Cip1), was altered in Stat5a-/- mammary cells, suggesting that one or more of these proteins mediate the effects of Stat5a in E+P-treated mammary epithelial cells.
Figures



References
-
- Howlin J, McBryan J, Martin F 2006 Pubertal mammary gland development: insights from mouse models. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11:283–297 - PubMed
-
- Brisken C, Rajaram RD 2006 Alveolar and lactogenic differentiation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11:239–248 - PubMed
-
- Darnell Jr JE 1997 STATs and gene regulation. Science 277:1630–1635 - PubMed
-
- Ihle JN 1996 STATs: signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84:331–334 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

