The A20 deubiquitinase activity negatively regulates LMP1 activation of IRF7
- PMID: 20392859
- PMCID: PMC2876664
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00364-10
The A20 deubiquitinase activity negatively regulates LMP1 activation of IRF7
Abstract
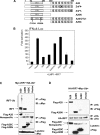
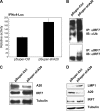
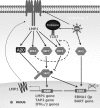
A20 possesses both deubiquitinase (DUB) and ubiquitin E3 ligase activities that are required for termination of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling leading to NF-kappaB activation and for blockage of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis. A20 is induced by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncoprotein LMP1. However, its dual ubiquitin-editing activities have not been investigated in the context of either EBV infection or IRF7 responses. Both A20 and IRF7 have oncogenic properties. We have recently shown that LMP1 activates IRF7 through K63-linked ubiquitination which requires RIP1 and TRAF6, but how this ubiquitination event is regulated has not been studied. Here, we show that A20 negatively regulates IRF7 transcriptional activity induced by LMP1. Deletion or mutation of A20 C-terminal zinc finger motifs had no effect on the inhibition of IRF7 activity, whereas DUB-deficient truncation or point mutation ablated the ability of A20 to inhibit IRF7. Correspondingly, the A20 N-terminal DUB domain, but not the C-terminal E3 ligase domain, interacts physically with IRF7. Transient expression of A20 reduced K63-linked ubiquitination of IRF7 in vivo, but an in vitro deubiquitination assay with purified constituents shows that IRF7 did not act as a substrate for A20 DUB activity. Moreover, A20 interacts with IRF7 endogenously in latently EBV-infected type 3 Raji cells, in which expression of both A20 and IRF7 is constitutively induced by the considerable level of endogenous LMP1. Knockdown of endogenous A20 in Raji cells by expression of A20 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) vectors increases endogenous IRF7 activity and ubiquitination, as well as the protein level of LMP1, a target of IRF7. Thus, A20 negatively regulates LMP1-stimulated IRF7 ubiquitination and activity in EBV latency, and its DUB activity is indispensable for this function. Finally, we discussed the regulation and function of IRFs in EBV latency.
Figures

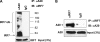

Similar articles
-
IRF7: activation, regulation, modification and function.Genes Immun. 2011 Sep;12(6):399-414. doi: 10.1038/gene.2011.21. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Genes Immun. 2011. PMID: 21490621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAF6 and the three C-terminal lysine sites on IRF7 are required for its ubiquitination-mediated activation by the tumor necrosis factor receptor family member latent membrane protein 1.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;28(20):6536-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00785-08. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18710948 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF1 Coordinates Polyubiquitin Signaling to Enhance Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Growth and Survival Pathway Activation.PLoS Pathog. 2015 May 21;11(5):e1004890. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004890. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25996949 Free PMC article.
-
The Linear Ubiquitin Assembly Complex Modulates Latent Membrane Protein 1 Activation of NF-κB and Interferon Regulatory Factor 7.J Virol. 2017 Jan 31;91(4):e01138-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01138-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27903798 Free PMC article.
-
The Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:119-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428373 Review.
Cited by
-
IRF7: activation, regulation, modification and function.Genes Immun. 2011 Sep;12(6):399-414. doi: 10.1038/gene.2011.21. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Genes Immun. 2011. PMID: 21490621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 regulates the function of interferon regulatory factor 7 by inducing its sumoylation.J Virol. 2012 Nov;86(22):12251-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01407-12. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22951831 Free PMC article.
-
The Central Role of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in EBV-Mediated Oncogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 26;14(3):611. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030611. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tryptophan-rich motif in the human parainfluenza virus type 2 V protein is critical for the blockade of toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)- and TLR9-dependent signaling.J Virol. 2011 May;85(9):4606-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02012-10. Epub 2011 Feb 23. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21345944 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 20 targets TRAF6 and human T cell leukemia virus type 1 tax to negatively regulate NF-kappaB signaling.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(13):6212-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00079-11. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21525354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balachandran, S., T. Venkataraman, P. B. Fisher, and G. N. Barber. 2007. Fas-associated death domain-containing protein-mediated antiviral innate immune signaling involves the regulation of IRF7. J. Immunol. 178:2429-2439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

