Cooperative activation of cyclin D1 and progesterone receptor gene expression by the SRC-3 coactivator and SMRT corepressor
- PMID: 20392877
- PMCID: PMC2875800
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0480
Cooperative activation of cyclin D1 and progesterone receptor gene expression by the SRC-3 coactivator and SMRT corepressor
Abstract
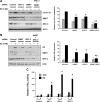
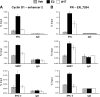
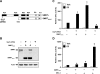
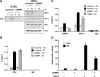
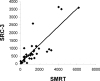
Although the ability of coactivators to enhance the expression of estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) target genes is well established, the role of corepressors in regulating 17beta-estradiol (E2)-induced gene expression is poorly understood. Previous studies revealed that the silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT) corepressor is required for full ERalpha transcriptional activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells, and we report herein the E2-dependent recruitment of SMRT to the regulatory regions of the progesterone receptor (PR) and cyclin D1 genes. Individual depletion of SMRT or steroid receptor coactivator (SRC)-3 modestly decreased E2-induced PR and cyclin D1 expression; however, simultaneous depletion revealed a cooperative effect of this coactivator and corepressor on the expression of these genes. SMRT and SRC-3 bind directly in an ERalpha-independent manner, and this interaction promotes E2-dependent SRC-3 binding to ERalpha measured by co-IP and SRC-3 recruitment to the cyclin D1 gene as measured by chromatin IP assays. Moreover, SMRT stimulates the intrinsic transcriptional activity of all of the SRC family (p160) coactivators. Our data link the SMRT corepressor directly with SRC family coactivators in positive regulation of ERalpha-dependent gene expression and, taken with the positive correlation found for SMRT and SRC-3 in human breast tumors, suggest that SMRT can promote ERalpha- and SRC-3-dependent gene expression in breast cancer.
Figures
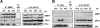


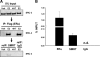
Similar articles
-
The silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT) corepressor is required for full estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(17):5933-48. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00237-07. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17591692 Free PMC article.
-
G protein pathway suppressor 2 (GPS2) is a transcriptional corepressor important for estrogen receptor alpha-mediated transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 25;284(52):36395-36404. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.062109. Epub 2009 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19858209 Free PMC article.
-
Unique roles of p160 coactivators for regulation of breast cancer cell proliferation and estrogen receptor-alpha transcriptional activity.Endocrinology. 2009 Apr;150(4):1588-96. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1001. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19095746 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin dependent kinase 2 and the regulation of human progesterone receptor activity.Steroids. 2007 Feb;72(2):202-9. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2006.11.025. Epub 2007 Jan 4. Steroids. 2007. PMID: 17207508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of SRC-3 in human breast cancer.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010 Feb;7(2):83-9. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.219. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20027190 Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of NCOR2 Inhibits Cell Proliferation via BDNF/TrkB/ERK in NF1-Derived MPNSTs.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;14(23):5798. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235798. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497280 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalein has protective effects on the 17β-estradiol-induced transformation of breast epithelial cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):10470-10484. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14433. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28060756 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor coactivators are coexpressed with steroid receptors and regulated by estradiol in mouse brain.Neuroendocrinology. 2011;94(1):49-57. doi: 10.1159/000323780. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Neuroendocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21311177 Free PMC article.
-
Progestin and antiprogestin responsiveness in breast cancer is driven by the PRA/PRB ratio via AIB1 or SMRT recruitment to the CCND1 and MYC promoters.Int J Cancer. 2015 Jun 1;136(11):2680-92. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29304. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25363551 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-regulated prohibitin is required for mouse uterine development and adult function.Endocrinology. 2011 Mar;152(3):1047-56. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0732. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21209023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katzenellenbogen BS 1996 Estrogen receptors: bioactivities and interactions with cell signaling pathways. Biol Reprod 54:287–293 - PubMed
-
- Sarrel PM, Lufkin EG, Oursler MJ, Keefe D 1994 Estrogen actions in arteries, bone and brain. Sci Am Sci Med 1:44–53
-
- Henderson BE, Ross R, Bernstein L 1988 Estrogens as a cause of human cancer: the Richard and Hinda Rosenthal Foundation Award Lecture. Cancer Res 48:246–253 - PubMed
-
- Glass CK 1994 Differential recognition of target genes by nuclear receptor monomers, dimers, and heterodimers. Endocr Rev 15: 391–407 - PubMed
-
- Oñate SA, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW 1995 Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 270:1354–1357 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

