First detection of an invasive Staphylococcus aureus strain (D958) with reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 20392906
- PMCID: PMC2884509
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00954-09
First detection of an invasive Staphylococcus aureus strain (D958) with reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
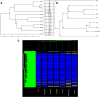
Strain D958, a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin, was isolated from a 69-year-old Saudi male patient presenting with severe sepsis immediately after admission. Despite high serum levels of vancomycin, the same S. aureus strain was isolated from five blood culture sets during 1 week. Treatment failure under therapeutic levels of vancomycin prompted us to investigate the resistance profile of this strain in further detail. The MIC values for vancomycin as determined by Etest and microdilution were 3.0 and 2.0 mg/liter, respectively, and remained unchanged during the treatment course. The macro-Etest method showed a MIC of 4 mg/liter. The strain showed liquid vancomycin and lysostaphin MBCs of 2.0 and 5.0 mg/liter, respectively. The isolates were confirmed as heterogeneously vancomycin-intermediate S. aureus (hVISA) by vancomycin population analysis profile. The areas under these curves were similar for Mu3 and D958 for vancomycin and teicoplanin (ratio values were 1 and 1.1 for vancomycin and teicoplanin, respectively). Extensive genotyping and molecular characterization demonstrated that the strain harbored a staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec element (SCCmec) type III cassette and was of sequence type ST241, a single-locus variant of the successful multiresistant clone ST239. Microarray results demonstrated that D958 contained numerous resistance determinants (generally plasmid or phage encoded). These results suggest that this strain is constitutively expressing an altered susceptibility to vancomycin. Further studies are warranted to assess the clonal distribution of such strains displaying reduced susceptibility to vancomycin prior to any antimicrobial therapy.
Figures
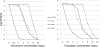
References
-
- Al-Mustafa, Z. H., and M. S. Al-Ghamdi. 2002. Use of antibiotics in the poultry industry in Saudi Arabia: implications for public health. Ann. Saudi Med. 22:4-7. - PubMed
-
- Andrade-Baiocchi, S., M. C. Tognim, O. C. Baiocchi, and H. S. Sader. 2003. Endocarditis due to glycopeptide-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus: case report and strain characterization. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 45:149-152. - PubMed
-
- Appelbaum, P. C. 2006. MRSA—the tip of the iceberg. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 12(Suppl. 2):3-10. - PubMed
-
- Ariza, J., M. Pujol, J. Cabo, C. Pena, N. Fernandez, J. Linares, J. Ayats, and F. Gudiol. 1999. Vancomycin in surgical infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with heterogeneous resistance to vancomycin. Lancet 353:1587-1588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

