Indirect immunofluorescence assay for intra vitam diagnosis of avian bornavirus infection in psittacine birds
- PMID: 20392921
- PMCID: PMC2884495
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00145-10
Indirect immunofluorescence assay for intra vitam diagnosis of avian bornavirus infection in psittacine birds
Abstract
Different avian bornavirus (ABV) genotypes have recently been detected in psittacine birds with proventricular dilatation disease (PDD), an inflammatory fatal central and peripheral nervous system disorder. An indirect immunofluorescence assay (IIFA) for intra vitam demonstration of ABV-specific serum antibodies was established since reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assays may not detect all ABV variants.
Figures
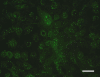
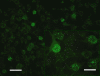
References
-
- Enderlein, D., S. Herzog, C. Herden, D. Neumann, T. Briese, E. F. Kaleta, M. Lierz, U. Heffels-Redmann, and H. Müller. 2009. Aviäres Bornavirus: Antikörper- und Genomnachweis in PDD positiven Vögeln, p. 18-20. In M. E. Krautwald-Junghanns and E. F. Kaleta (ed.), Tagungsbericht 1. DVG-Tagung über Vogel- und Reptilienkrankheiten 25.-27.09.09. DVG-Verlag, Geissen, Germany.
-
- Gancz, A. Y., A. L. Kistler, A. L. Greninger, Y. Farnoushi, S. Mechani, S. Perl, A. Berkowitz, N. Perez, S. Clubb, J. L. DeRisi, D. Ganam, and A. Lublin. 2009. Experimental induction of proventricular dilatation disease in cockatiels (Nymphicus hollandicus) inoculated with brain homogenates containing avian bornavirus 4. Virol. J. 6:100. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herden, C., S. Herzog, T. Wehner, C. Zink, J. A. Richt, and K. Frese. 1999. Comparison of different methods of diagnosing Borna disease in horses post mortem, p. 286-290. In U. Wernery, J. Wade, J. A. Mumford, and O. R. Kaaden (ed.), Equine infectious diseases VIII. R&W Publications, Newmarket, United Kingdom.
-
- Honkavuori, K. S., H. L. Shivaprasad, B. L. Williams, P. L. Quan, M. Hornig, C. Street, G. Palacios, S. K. Hutchison, M. Franca, M. Egholm, T. Briese, and W. I. Lipkin. 2008. Novel Borna virus in psittacine birds with proventricular dilatation disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 14:1883-1886. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaaden, O. R., S. Lange, and B. Stiburek. 1982. Establishment and characterization of chicken embryo fibroblast clone LSCC-H32. In Vitro 18:827-834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

